Burger King 2006 Annual Report Download - page 100
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 100 of the 2006 Burger King annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
BURGER KING HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements Ì (Continued)
For the year ended June 30, 2006, the valuation allowance increased by $11 million. After considering the
level of historical taxable income, projections for future taxable income over the periods in which the deferred
tax assets are deductible, and the reversal of deferred tax liabilities, management believes it is more likely than
not that the benefits of certain state and foreign net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets
will not be realized.
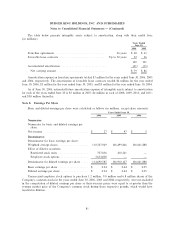
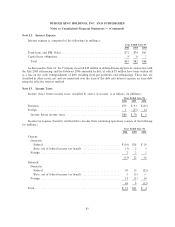
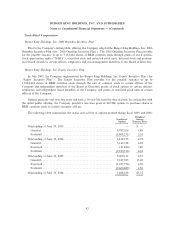
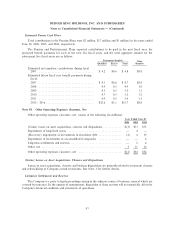
Changes in valuation allowance for the years ended June 30, 2006, 2005 and 2004 are as follows:
Years Ended June 30,
2006 2005 2004
Beginning balanceÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏ $78 $65 $22
Purchase accounting adjustments ÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏ Ì Ì 31
Change in estimates recorded to deferred income tax expense ÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏ 1 8 8
Change in estimates in valuation allowance recorded to intangible assets ÏÏ (12) Ì (2)
Change due to increase in deferred tax assets that are fully reserved ÏÏÏÏÏ 20 5 Ì
Changes from foreign currency exchange rates ÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏ 2 Ì 6
Ending balance ÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏÏ $89 $78 $65
The Company has no federal loss carryforwards in the United States and has state loss carryforwards of
$37 million, expiring between 2007 and 2025. In addition, the Company has foreign loss carryforwards of
$83 million expiring between 2007 and 2019, and foreign loss carryforwards of $131 million that do not expire.
Deferred taxes have not been provided on basis difference related to investments in foreign subsidiaries.
These differences consist primarily of $19 million of undistributed earnings, which are considered to be
permanently reinvested in the operations of such subsidiaries.
As a matter of course, the Company is regularly audited by various tax authorities. From time to time,
these audits result in proposed assessments where the ultimate resolution may result in the Company owing
additional taxes. The Company believes that its tax positions comply with applicable tax law and that it has
adequately provided for these matters.
During 2006, the Company regionalized the activities associated with managing its European and Asian
businesses, including the transfer of rights of existing franchise agreements, the ability to grant future
franchise agreements and utilization of the Company's intellectual property assets in EMEA/APAC, in new
European and Asian holding companies. The new holding companies acquired the intellectual property rights
from BKC, a U.S. company, in a transaction that generated a taxable gain for BKC in the United States of
$328 million resulting in a $126 million tax liability. This liability is recorded in other accrued liabilities in the
consolidated balance sheet and is offset by $40 million through the utilization of net operating loss
carryforwards and other foreign tax credits, resulting in a cash tax payment obligation of $86 million, which
the Company expects to make in the first quarter of fiscal 2007. In accordance with the guidance provided by
ARB 51, Consolidated Financial Statements, the resulting tax amount of $126 million was recorded as a
prepaid tax asset and offset by the reversal of a $105 million deferred tax liability, which the Company had
previously recorded associated with the transferred asset resulting in a net prepaid asset of $21 million, which
is included in other assets, net on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
Note 14. Related Party Transactions
In connection with the Company's acquisition of BKC, the Company entered into a management
agreement with the Sponsors for monitoring the Company's business through board of director participation,
executive team recruitment, interim senior management services and other services consistent with arrange-
ments with private equity funds (""the management agreement''). Pursuant to the management agreement,
88