Audi 2010 Annual Report Download - page 236
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 236 of the 2010 Audi annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263
 |
 |
234
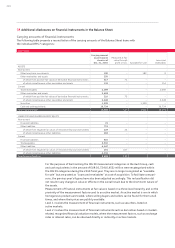
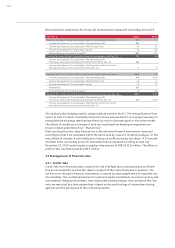
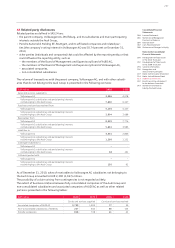
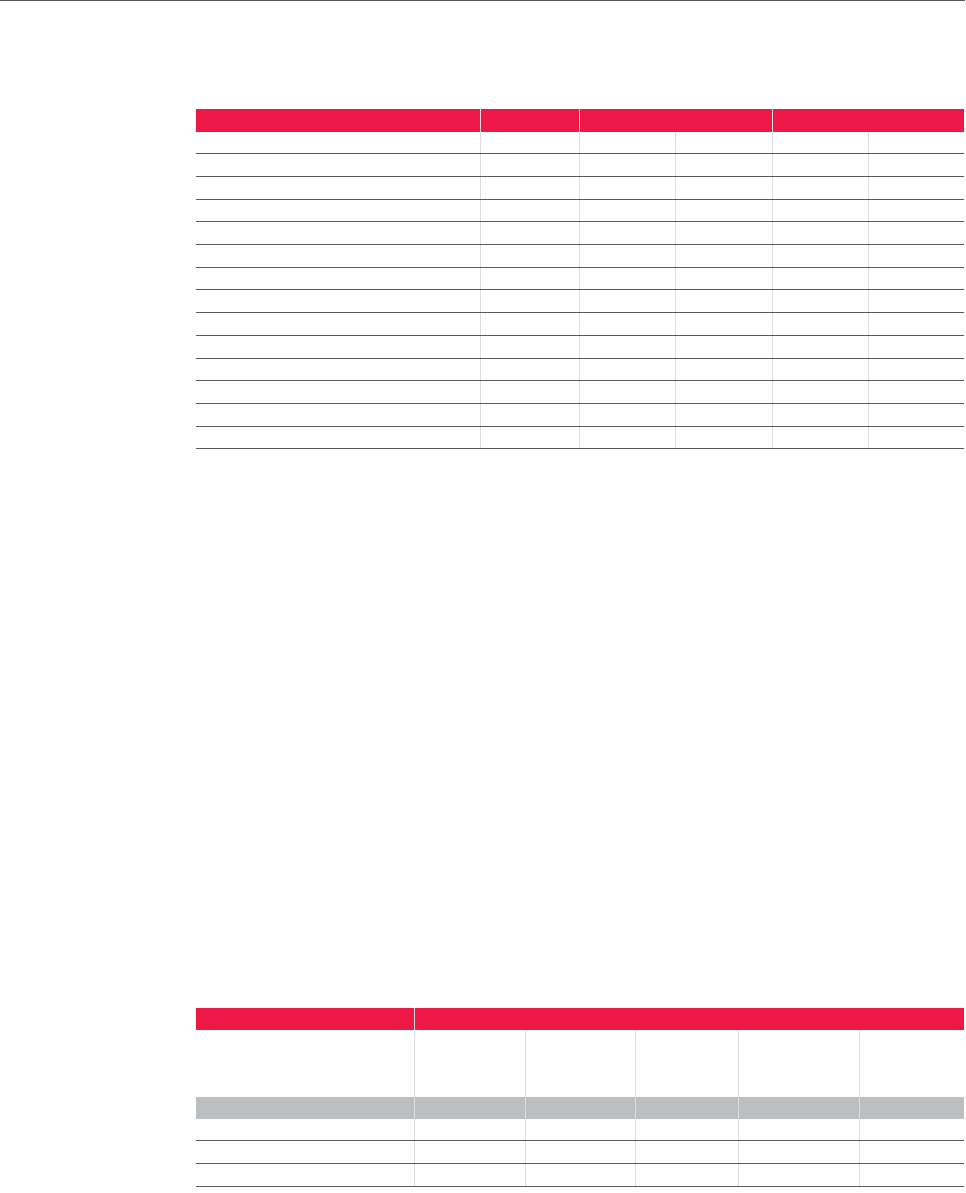
The sensitivity analyses carried out enabled the following other market risks to be quantified for
the Audi Group:
Data in 2010 2009
Fund price risks
Change in share prices Percent + 10 – 10 + 10 – 10
Effects on equity capital EUR million 8 – 9 4 – 4
Commodity price risks
Change in commodity prices Percent + 10 – 10 + 10 – 10
Effects on equity capital EUR million 46 – 46 41 – 41
Effects on results EUR million 44 – 44 16 – 16
Interest rate change risks
Change in market interest rate Basis points + 100 – 100 + 100 – 100
Effects on equity capital EUR million – 12 14 – 11 12
Effects on results EUR million 7 – 8 – 3 4
Residual value risks
Change in market prices of used cars Percent + 10 – 10 + 10 – 10
Effects on results EUR million 226 – 127 200 – 46
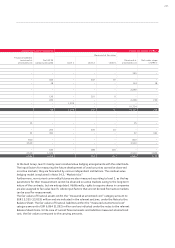
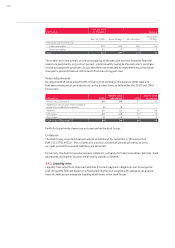
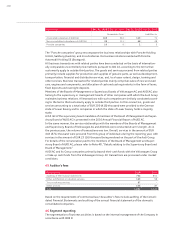
34.4 Methods of monitoring the effectiveness of hedging relationships
Within the Audi Group, the effectiveness of hedging relationships is evaluated prospectively
using the critical terms match method, as well as by means of statistical methods in the form of
a regression analysis. Retrospective evaluation of the effectiveness of hedges involves an effec-
tiveness test in the form of the dollar offset method or in the form of a regression analysis.
In the case of the dollar offset method, the changes in value of the underlying transaction,
expressed in monetary units, are compared with the changes in value of the hedge, expressed
in monetary units. All hedge relationships were effective within the range specified in IAS 39
(80 to 125 percent).
In the case of regression analysis, the performance of the underlying transaction is viewed as an
independent variable, while that of the hedging transaction is regarded as a dependent variable.
The transaction is classed as effective hedging if the coefficients of determination and escalation
factors are appropriate. All of the hedging relationships verified using this statistical method
proved to be effective as of the year-end date.
In 2010, there was ineffectiveness resulting from cash flow hedges amounting to
EUR 10 (3) million.
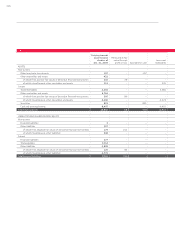
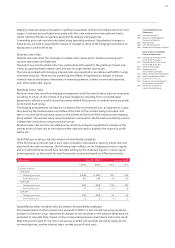
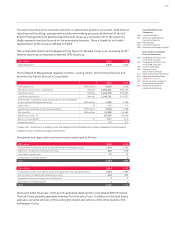
Nominal volume of cash flow hedges
The nominal volumes of the presented cash flow hedges for hedging currency risks and com-
modity price risks represent the total of all buying and selling prices on which the transactions
are based.
EUR million Nominal volumes
Dec. 31, 2010
Residual time
to maturity up
to 1 year
Residual time
to maturity
up to 5 years
Residual time to
maturity more
than 5 years Dec. 31, 2009
Cash flow hedges 21,664 6,508 15,129 28 9,289
Foreign exchange contracts 20,330 5,692 14,624 14 7,143
Currency option transactions 989 728 261 – 1,806
Commodity futures 345 87 244 14 340
The derivative financial instruments used exhibit a maximum hedging term of six years.
