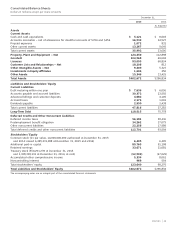
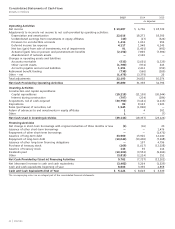
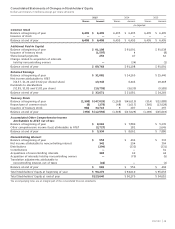
AT&T Wireless 2015 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2015 AT&T Wireless annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
AT&T INC.
|
35
use of interest rate swaps. We have established interest rate
risk limits that we closely monitor by measuring interest rate
sensitivities in our debt and interest rate derivatives portfolios.
Most of our foreign-denominated long-term debt has been
swapped from fixed-rate or floating-rate foreign currencies
to fixed-rate U.S. dollars at issuance through cross-currency
swaps, removing interest rate risk and foreign currency
exchange risk associated with the underlying interest and
principal payments. Likewise, periodically we enter into interest
rate locks to partially hedge the risk of increases
in the benchmark interest rate during the period leading
up to the probable issuance of fixed-rate debt. We expect
gains or losses in our cross-currency swaps and interest
rate locks to offset the losses and gains in the financial
instruments they hedge.
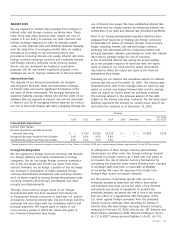
Following are our interest rate derivatives subject to material
interest rate risk as of December 31, 2015. The interest rates
illustrated below refer to the average rates we expect to pay
based on current and implied forward rates and the average
rates we expect to receive based on derivative contracts.
The notional amount is the principal amount of the debt
subject to the interest rate swap contracts. The fair value asset
(liability) represents the amount we would receive (pay) if we
had exited the contracts as of December 31, 2015.
MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risks primarily from changes in
interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates. These
risks, along with other business risks, impact our cost of
capital. It is our policy to manage our debt structure and
foreign exchange exposure in order to manage capital
costs, control financial risks and maintain financial flexibility
over the long term. In managing market risks, we employ
derivatives according to documented policies and
procedures, including interest rate swaps, interest rate locks,
foreign currency exchange contracts and combined interest
rate foreign currency contracts (cross-currency swaps).
We do not use derivatives for trading or speculative
purposes. We do not foresee significant changes in the
strategies we use to manage market risk in the near future.
Interest Rate Risk
The majority of our financial instruments are medium-
and long-term fixed-rate notes and debentures. Changes
in interest rates can lead to significant fluctuations in the
fair value of these instruments. The principal amounts by
expected maturity, average interest rate and fair value of our
liabilities that are exposed to interest rate risk are described
in Notes 9 and 10. In managing interest expense, we control
our mix of fixed and floating rate debt, principally through the
Maturity
Fair Value
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Thereafter Total 12/31/15
Interest Rate Derivatives
Interest Rate Swaps:
Receive Fixed/Pay Variable Notional
Amount Maturing $ — $ 700 $3,000 $3,350 $ — $ — $7,050 $136
Weighted-Average Variable Rate Payable1 3.4% 4.0% 4.5% 3.8% — —
Weighted-Average Fixed Rate Receivable 4.5% 4.5% 4.5% 3.5% — —
1 Interest payable based on current and implied forward rates for One, Three, or Six Month LIBOR plus a spread ranging between approximately 14 and 425 basis points.
In anticipation of other foreign currency-denominated
transactions, we often enter into foreign exchange forward
contracts to provide currency at a fixed rate. Our policy is
to measure the risk of adverse currency fluctuations by
calculating the potential dollar losses resulting from changes
in exchange rates that have a reasonable probability
of occurring. We cover the exposure that results from
changes that exceed acceptable amounts.
For the purpose of assessing specific risks, we use a
sensitivity analysis to determine the effects that market
risk exposures may have on the fair value of our financial
instruments and results of operations. To perform the
sensitivity analysis, we assess the risk of loss in fair values
from the effect of a hypothetical 10% fluctuation of the
U.S.dollar against foreign currencies from the prevailing
foreign currency exchange rates, assuming no change in
interest rates. We have foreign exchange forward contracts,
maturing on February 25, 2016, held by our GSF Telecom and
Nextel Mexico subsidiaries (AT&T Telecom Holdings S. de R.L.
de C.V. & AT&T Comunicaciones Digitales S. de R.L. de C.V.).
Foreign Exchange Risk
We are exposed to foreign currency exchange risk through
our foreign affiliates and equity investments in foreign
companies. We do not hedge foreign currency translation
risk in the net assets and income we report from these
sources. However, we do hedge a portion of the exchange
risk involved in anticipation of highly probable foreign
currency-denominated transactions and cash flow streams,
such as those related to issuing foreign-denominated debt,
receiving dividends from foreign investments, and other
receipts and disbursements.
Through cross-currency swaps, most of our foreign-
denominated debt has been swapped from fixed-rate
or floating-rate foreign currencies to fixed-rate U.S. dollars
at issuance, removing interest rate risk and foreign currency
exchange risk associated with the underlying interest and
principal payments. We expect gains or losses in our
cross-currency swaps to offset the losses and gains in
the financial instruments they hedge.