Singapore Airlines 2007 Annual Report Download - page 92
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 92 of the 2007 Singapore Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Singapore Airlines 90 Annual Report 2006-07
2 Accounting Policies (continued)
(ac)
Derivative fi nancial instruments and hedging (continued)
The fair value of forward currency contracts is determined by reference to current forward prices for contracts with
similar maturity profi les. The fair value of interest rate contracts is calculated using rates assuming these contracts
are liquidated at balance sheet date. The fair value of jet fuel swap contracts is determined by reference to market
values for similar instruments. The fair value of jet fuel option contracts is determined by reference to available
market information and option valuation methodology.
At the inception of a hedge relationship, the Group formally designates and documents the hedge relationship to
which the Group wishes to apply hedge accounting and the risk management objective and strategy for undertaking
the hedge. The documentation includes identifi cation of the hedged item or transaction, the hedging instrument, the
nature of the risk being hedged and how the entity will assess the hedging instrument’s effectiveness in offsetting
the exposure to changes in the hedged item’s (or transaction’s) cash fl ows attributable or fair values to the hedged
risk. Such hedges are expected to be highly effective in achieving offsetting changes in cash fl ows or fair value,
and are assessed on an ongoing basis to determine that they have been highly effective throughout the fi nancial
reporting periods for which they are designated.
Hedges which meet the criteria for hedge accounting are accounted for as follows:
Cash fl ow hedges
For cash fl ow hedges, the effective portion of the gain or loss on the hedging instrument is recognised directly in the
fair value reserve (Note 14), while the ineffective portion is recognised in the profi t and loss account.
Amounts taken to the fair value reserve are transferred to the profi t and loss account when the hedged transaction
affects profi t or loss, such as when a forecast sale or purchase occurs. If the hedged item is the cost of a non-
fi nancial asset or liability, the amounts taken to the fair value reserve are transferred to the initial carrying amount
of the non-fi nancial asset or liability.
Fair value hedges
For fair value hedges, the gain or loss on the hedging instrument is taken directly to profi t and loss account.
(ad)
Segmental reporting
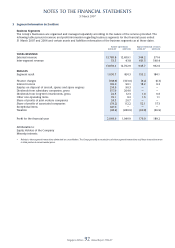
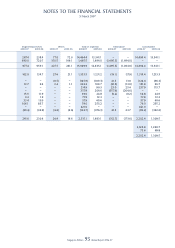
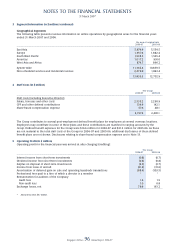
(i) Business segment
The Group’s businesses are organised and managed separately accordingly to the nature of the services
provided. The signifi cant business segments of the Group are airline operations, airport terminal services and
engineering services.
(ii) Geographical segment
The analysis of revenue by area of original sale from airline operations is derived by allocating revenue to the
area in which the sale was made. Revenue from other operations, which consists principally of airport terminal
services and engineering services, is derived in Singapore and therefore, is not shown.
Assets, which consist principally of fl ight and ground equipment, support the entire worldwide transportation
system, are mainly located in Singapore. An analysis of assets and capital expenditure of the Group by
geographical distribution has therefore not been included.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
31 March 2007