Volvo 2002 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2002 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
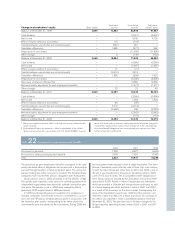
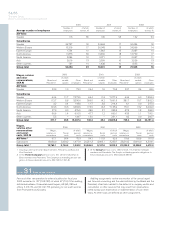
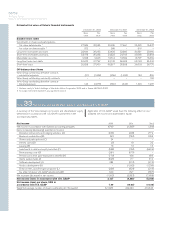
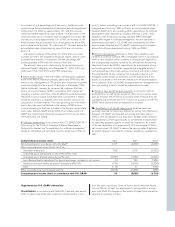
Volvo Group outstanding derivatives – financial exposure
December 31, 2000 December 31, 2001 December 31, 2002
Notional Book Estimated Notional Book Estimated Notional Book Estimated
amount value fair value amount value fair value amount value fair value
Interest-rate swaps
– receivable
position 64,345 561 2,990 62,456 3,670 4,549 78,571 2,822 4,404
– payable position 57,488 (366) (2,969) 86,328 (3,888) (4,633) 73,257 (1,568) (2,536)
Forwards and futures
– receivable
position 174,576 0 201 230,323 120 120 260,921 216 216
– payable position 201,657 (28) (247) 250,390 (126) (126) 255,503 (217) (220)
Foreign exchange
derivative contracts
– receivable
position 32,741 34 1,046 6,306 96 100 15,962 211 202
– payable position 21,668 (76) (2,894) 21,465 (428) (435) 5,443 (70) (72)
Options purchased,
caps and floors
– receivable
position 52 – 1––––––
– payable position ––––––200–(7)
Options written,
caps and floors
– receivable
position –––––––––
– payable position 55 – 0––––––
Total 125 (1,873) (556) (425) 1,394 1,987
Credit risks in financial instruments
Credit risk in financial investments
The liquidity in the Group is invested mainly in local cash pools or
directly with Volvo Treasury. Volvo Treasury invests the liquid funds in
the money and capital markets. This concentrates the credit risk
within the Group’s in-house bank.
All investments must meet criteria for low credit risk and high li-
quidity. In accordance with Volvo’s credit policy, counterparties for both
investments and transactions in derivatives must in general have
received a rating of “A” or better from one of the well-established
credit-rating institutions.
Counterparty risks
The derivative instruments used by Volvo to reduce its foreign-
exchange and interest-rate risk in turn give rise to a counterparty
risk, the risk that a counterparty will not fulfill its part of a forward or
option contract, and that a potential gain will not be realized.
Transactions with derivative instruments are mainly conducted via
Volvo Treasury which means that the counterparty risk is concentrated
within the Group’s in-house bank. Where appropriate, the Volvo
Group arranges master netting agreements with the counterparty to
reduce exposure. The credit exposure in interest-rate and foreign
exchange contracts is represented by the positive fair value – the
potential gain on these contracts – as of the reporting date. The risk
exposure is calculated daily. The credit risk in futures contracts is
limited through daily or monthly cash settlements of the net change
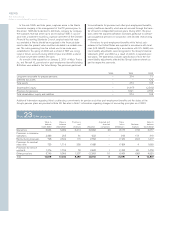
in value of open contracts. The estimated exposure in foreign
exchange contracts, interest-rate swaps and futures, options and
commodity forward contracts amounted to 1,219; 4,620; 94 and
272 as of December 31, 2002.
Volvo does not have any significant exposure to an individual cus-
tomer or counterparty.
Calculation of fair value of financial instruments
Volvo has used generally accepted methods to calculate the market
value of the Group’s financial instruments as of December 31, 2000,
2001 and 2002. In the case of instruments with maturities shorter
than three months – such as liquid funds and certain current liabil-
ities as well as certain short-term loans – the book value has been
assumed to closely approximate market value.
Official exchange rates and prices quoted in the open market
have been used initially for purposes of valuation. In their absence,
the valuation has been made by discounting future cash flows at the
market interest rate for each maturity. These values are estimates
and will not necessarily be realized.