US Airways 2003 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2003 US Airways annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
If the Company is unable to meet the aforementioned financial covenants, as amended, it would be in default under the ATSB Loan and the
Stabilization Board has the right to accelerate the ATSB Loan and exercise other remedies against US Airways. Such acceleration would have a material
adverse effect on the Company's future liquidity, results of operation and financial condition.
In November 2001, the Company obtained a $404 million credit facility from General Electric (GE Credit Facility) secured by collateral including 11
A320-family aircraft and 28 spare engines. As discussed below, the terms of this credit facility were renegotiated so that borrowings bear interest rates of
LIBOR plus 3.5% and the term of the facility was extended from 2006 to 2012.
GE is the Company's largest creditor. In addition to the GE Credit Facility, GE has provided financing or guarantees on 121 of the Company's current
operating aircraft. It also maintains the engines on the Company's B737-family aircraft, A320-family aircraft and B767 aircraft. In connection with its
reorganization under Chapter 11, the Company reached a settlement with GE that resolved substantially all aircraft, aircraft engine and loan-related issues.
The Company obtained additional financing from GE in the form of a liquidity facility of up to $360 million (GE Liquidity Facility). Borrowings under the
liquidity facility bear interest of LIBOR plus 4.25%. GE received warrants to purchase 3,817,500 shares of Class A Common Stock at $7.42 per share in
Reorganized US Airways Group. GE subsequently agreed to provide committed financing for up to 70 regional jets or $1.4 billion utilizing lease equity and/
or mortgage debt.
Every obligation of the Company to GE is generally cross-defaulted to all GE obligations including the GE Credit Facility and is cross-collateralized to
the collateral securing the GE Credit Facility.
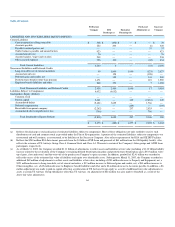
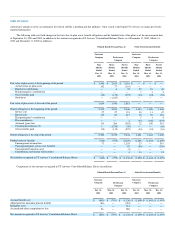
Debt outstanding as of December 31, 2002 included $300 million of drawings under the RSA DIP Facility. This obligation was satisfied upon
emergence from bankruptcy.
Interest rates on $1.53 billion principal amount of long-term debt as of December 31, 2003 are subject to adjustment to reflect changes in floating
interest rates.
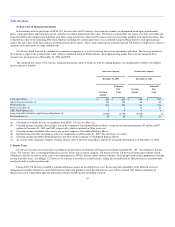
7. Employee Pension and Benefit Plans
Substantially all of US Airways' employees meeting certain service and other requirements are eligible to participate in various pension, medical,
dental, life insurance, disability and survivorship plans.
(a) Defined benefit and other postretirement benefit plans
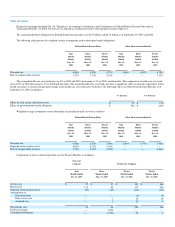
US Airways sponsors several qualified defined benefit plans and other postretirement benefit plans for certain employees. Effective March 31, 2003,
US Airways terminated its qualified and nonqualified pilot defined benefit pension plans. The PBGC was appointed trustee of the qualified plan effective with
the termination. Liabilities related to pension plans covering foreign employees are calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
and funded in accordance with the laws of the individual country.
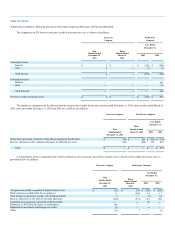
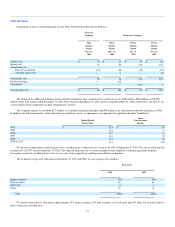
In December 2003, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003 (the Medicare Prescription Drug Act) became law in
the United States. The Medicare Prescription Drug Act introduces a prescription drug benefit under Medicare as well as a federal subsidy to sponsors of
retiree health care benefit plans that provide a benefit that is at least actuarially equivalent to the Medicare benefit. In accordance with FASB Staff Position
FAS 106-1, "Accounting and Disclosure Requirements Related to the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003," US
Airways has elected to defer recognition of the effects of the Medicare Prescription Drug Act in measuring its benefit obligation or cost. Specific
72