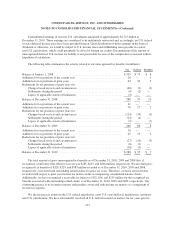
UPS 2010 Annual Report Download - page 117
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 117 of the 2010 UPS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.UNITED PARCEL SERVICE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
NOTE 14. DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS AND RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Management Policies
We are exposed to market risk, primarily related to foreign exchange rates, commodity prices and interest
rates. These exposures are actively monitored by management. To manage the volatility relating to certain of
these exposures, we enter into a variety of derivative financial instruments. Our objective is to reduce, where it is
deemed appropriate to do so, fluctuations in earnings and cash flows associated with changes in foreign currency
rates, commodity prices and interest rates. It is our policy and practice to use derivative financial instruments
only to the extent necessary to manage exposures. As we use price sensitive instruments to hedge a certain
portion of our existing and anticipated transactions, we expect that any loss in value for those instruments
generally would be offset by increases in the value of those hedged transactions. We do not hold or issue
derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes.
Credit Risk Management
The forward contracts, swaps, and options discussed below contain an element of risk that the counterparties
may be unable to meet the terms of the agreements. However, we minimize such risk exposures for these
instruments by limiting the counterparties to banks and financial institutions that meet established credit
guidelines, and monitoring counterparty credit risk to prevent concentrations of credit risk with any single
counterparty.
We have agreements with some of our counterparties containing early termination rights and bilateral
collateral provisions, whereby security is required if market risk exposure exceeds a specified threshold amount
or credit ratings fall below certain levels. As of December 31, 2010, we had not posted nor received any
collateral under these contractual provisions. The remaining counterparty agreements contain early termination
rights but no bilateral collateral provisions.
We have not historically incurred, and do not expect to incur in the future, any losses as a result of
counterparty default.
Accounting Policy for Derivative Instruments
We recognize all derivative instruments as assets or liabilities in the balance sheet at fair value. The
accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative instrument depends on whether it has been designated and
qualifies as part of a hedging relationship and, further, on the type of hedging relationship. For those derivative
instruments that are designated and qualify as hedging instruments, a company must designate the derivative,
based upon the exposure being hedged, as a cash flow hedge, a fair value hedge, or a hedge of a net investment in
a foreign operation.
A cash flow hedge refers to hedging the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows that is
attributable to a particular risk. For derivative instruments that are designated and qualify as a cash flow hedge,
the effective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative instrument is reported as a component of AOCI, and
reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The remaining
gain or loss on the derivative instrument in excess of the cumulative change in the present value of future cash
flows of the hedged item, or hedge components excluded from the assessment of effectiveness, are recognized in
the income statement during the current period.
105