U-Haul 2016 Annual Report Download - page 44
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 44 of the 2016 U-Haul annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
38
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to financial market risks, including changes in interest rates and currency exchange
rates. To mitigate these risks, we may utilize derivative financial instruments, among other strategies. We
do not use derivative financial instruments for speculative purposes.
Interest Rate Risk
The exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates relates primarily to our variable rate debt
obligations and one variable rate operating lease. We have used interest rate swap agreements and
forward swaps to reduce our exposure to changes in interest rates. We enter into these arrangements
with counterparties that are significant financial institutions with whom we generally have other financial
arrangements. We are exposed to credit risk should these counterparties not be able to perform on their
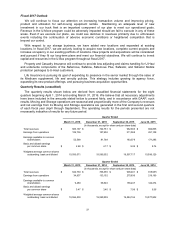
obligations. Following is a summary of our interest rate swaps agreements at March 31, 2016:
Notional
Amount
Fair Value
Effective
Date
Expiration
Date
Fixed
Rate
Floating Rate
(In thousands)
$
204,166
$
(13,322)
8/18/2006
8/10/2018
5.43%
1 Month LIBOR
5,450
(a)
(101)
8/15/2010
7/15/2017
2.15%
1 Month LIBOR
10,313
(a)
(328)
6/1/2011
6/1/2018
2.38%
1 Month LIBOR
20,542
(a)
(485)
8/15/2011
8/15/2018
1.86%
1 Month LIBOR
8,300
(a)
(181)
9/12/2011
9/10/2018
1.75%
1 Month LIBOR
9,338
(b)
(142)
3/28/2012
3/28/2019
1.42%
1 Month LIBOR
11,458
(142)
4/16/2012
4/1/2019
1.28%
1 Month LIBOR
21,825
(144)
1/15/2013
12/15/2019
1.07%
1 Month LIBOR
(a) forward swap
(b) operating lease
As of March 31, 2016, we had $770.0 million of variable rate debt obligations and $9.3 million of a
variable rate operating lease. If the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate were to increase 100 basis points, the
increase in interest expense on the variable rate debt and a variable rate operating lease would decrease
future earnings and cash flows by $3.6 million annually (after consideration of the effect of the above
derivative contracts). Certain senior mortgages have an anticipated repayment date and a maturity date.
If these senior mortgages are not repaid by the anticipated repayment date the interest rate on these
mortgages would increase from the current fixed rate. We are using the anticipated repayment date for
our maturity schedule.
Additionally, our insurance subsidiaries’ fixed income investment portfolios expose us to interest rate
risk. This interest rate risk is the price sensitivity of a fixed income security to changes in interest rates. As
part of our insurance companies’ asset and liability management, actuaries estimate the cash flow
patterns of our existing liabilities to determine their duration. These outcomes are compared to the
characteristics of the assets that are currently supporting these liabilities assisting management in
determining an asset allocation strategy for future investments that management believes will mitigate the
overall effect of interest rates.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
The exposure to market risk for changes in foreign currency exchange rates relates primarily to our
Canadian business. Approximately 4.4%, 5.2% and 5.4% of our revenue was generated in Canada in
fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The result of a 10% change in the value of the U.S. dollar
relative to the Canadian dollar would not be material to net income. We typically do not hedge any foreign
currency risk since the exposure is not considered material.