HP 2005 Annual Report Download - page 79
Download and view the complete annual report
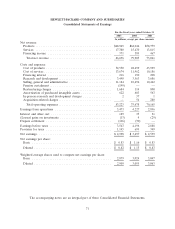
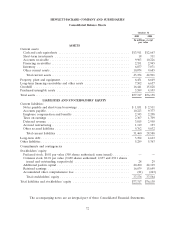
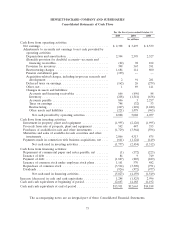
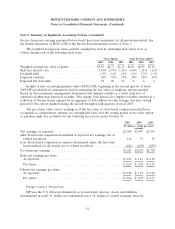
Please find page 79 of the 2005 HP annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Hewlett-Packard Company, its
wholly-owned subsidiaries and its controlled majority-owned subsidiaries (collectively, ‘‘HP’’). HP
accounts for equity investments in companies over which HP has the ability to exercise significant
influence, but does not hold a controlling interest, under the equity method, and HP records its
proportionate share of income or losses in Interest and other, net in the Consolidated Statements of
Earnings. HP has eliminated all significant intercompany accounts and transactions.
Reclassifications and Segment Reorganization
HP has made certain reclassifications to prior year amounts in order to conform to the current
year presentation. In addition, HP reclassified certain information technology (‘‘IT’’) infrastructure
costs from selling, general and administrative expenses to cost of products, cost of services and research
and development expenses to align the IT costs better with the functional areas they support. The
impact of these reclassifications is an increase in cost of sales offset by an equal reduction of operating
expenses, with no impact on consolidated or segment level earnings from operations.
HP has revised the presentation of its Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the fiscal year
ended October 31, 2004 to reflect the gross purchases and sales of auction rate securities within cash
flows from investing activities. This change does not affect previously reported subtotals within the
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, or previously reported results of operations for any period
presented.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting
principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in
HP’s Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ materially
from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
HP recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of a sales arrangement exists, delivery occurs or
services are rendered, the sales price or fee is fixed or determinable and collectibility is reasonably
assured. When a sales arrangement contains multiple elements, such as hardware and software
products, licenses and/or services, HP allocates revenue to each element based on its relative fair value.
Fair value for software is determined based on vendor specific objective evidence (‘‘VSOE’’) or, in the
absence of VSOE for all the elements, the residual method when VSOE exists for all the undelivered
elements. In the absence of fair value for a delivered element, HP first allocates revenue to the fair
value of the undelivered elements and the residual revenue to the delivered elements. Where the fair
value for an undelivered element cannot be determined, HP defers revenue for the delivered elements
until the undelivered elements are delivered. HP limits the amount of revenue recognition for delivered
elements to the amount that is not contingent on the future delivery of products or services or subject
to customer-specified return or refund privileges.
HP ceases revenue recognition on delinquent accounts based upon a number of factors, including
customer credit history, number of days past due and the terms of the customer agreement. HP
75