Berkshire Hathaway 2012 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
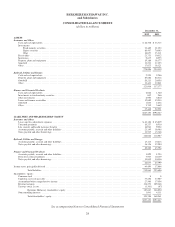
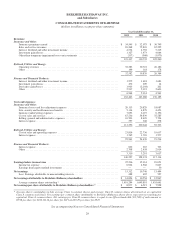
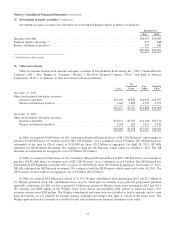
Please find page 39 of the 2012 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(p) Regulated utilities and energy businesses (Continued)
Regulatory assets and liabilities are continually assessed for probable future inclusion in regulatory rates by
considering factors such as applicable regulatory or legislative changes and recent rate orders received by other
regulated entities. If future inclusion in regulatory rates ceases to be probable, the amount no longer probable of
inclusion in regulatory rates is charged to earnings or reflected as an adjustment to rates.
(q) Life, annuity and health insurance benefits
The liability for insurance benefits under life contracts has been computed based upon estimated future investment
yields, expected mortality, morbidity, and lapse or withdrawal rates and reflects estimates for future premiums and
expenses under the contracts. These assumptions, as applicable, also include a margin for adverse deviation and may
vary with the characteristics of the reinsurance contract’s date of issuance, policy duration and country of risk. The
interest rate assumptions used may vary by reinsurance contract or jurisdiction and generally range from approximately
3% to 7%. Annuity contracts are discounted based on the implicit rate of return as of the inception of the contracts and
such interest rates range from approximately 1% to 7%.
(r) Foreign currency
The accounts of our non-U.S. based subsidiaries are measured in most instances using the local currency of the
subsidiary as the functional currency. Revenues and expenses of these businesses are generally translated into U.S.
Dollars at the average exchange rate for the period. Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate as of the
end of the reporting period. Gains or losses from translating the financial statements of foreign-based operations are
included in shareholders’ equity as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income. Gains and losses arising
from transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency of the entity that is party to the
transaction are included in earnings.
(s) Income taxes
Berkshire files a consolidated federal income tax return in the United States, which includes our eligible subsidiaries.
In addition, we file income tax returns in state, local and foreign jurisdictions as applicable. Provisions for current
income tax liabilities are calculated and accrued on income and expense amounts expected to be included in the income
tax returns for the current year. Income taxes reflected in earnings also include deferred income tax provisions for the
temporary differences between income and expense amounts includable in current income tax returns and amounts
reported for financial reporting purposes.
Deferred income taxes are calculated under the liability method. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are
computed on differences between the financial statement bases and tax bases of assets and liabilities at the enacted tax
rates. Changes in deferred income tax assets and liabilities that are associated with components of other comprehensive
income are charged or credited directly to other comprehensive income. Otherwise, changes in deferred income tax
assets and liabilities are included as a component of income tax expense, as deferred income tax expense. The effect on
deferred income tax assets and liabilities attributable to changes in enacted tax rates are charged or credited to income
tax expense in the period of enactment. Valuation allowances are established for certain deferred tax assets where
realization is not likely.
Assets and liabilities are established for uncertain tax positions taken or positions expected to be taken in income tax
returns when such positions are judged to not meet the “more-likely-than-not” threshold based on the technical merits
of the positions. Estimated interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions are generally included as a
component of income tax expense.
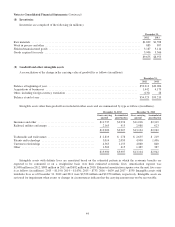
(t) New accounting pronouncements
As of January 1, 2012, we adopted ASU 2010-26, “Accounting for Costs Associated with Acquiring or Renewing
Insurance Contracts”, which specifies that only direct incremental costs associated with successful efforts in acquiring
or renewing of insurance contracts should be capitalized and amortized over the policy term. All other costs are
required to be expensed as incurred. Capitalized costs include certain advertising costs if the primary purpose of the
advertising is to elicit sales to customers who could be shown to have responded directly to the advertising and the
probable future revenues generated are in excess of expected future costs to be incurred in realizing those revenues.
37