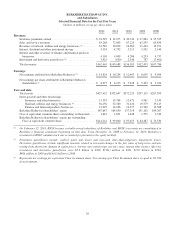
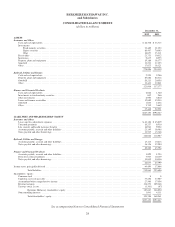
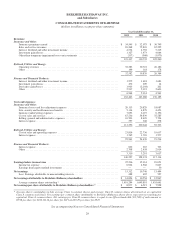
Berkshire Hathaway 2012 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2012 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(f) Derivatives
We carry derivative contracts at estimated fair value. Such balances reflect reductions permitted under master netting
agreements with counterparties. The changes in fair value of derivative contracts that do not qualify as hedging
instruments for financial reporting purposes are recorded in earnings.
Cash collateral received from or paid to counterparties to secure derivative contract assets or liabilities is included in
other liabilities or other assets. Securities received from counterparties as collateral are not recorded as assets and
securities delivered to counterparties as collateral continue to be reflected as assets in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
(g) Fair value measurements
As defined under GAAP, fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability
between market participants in the principal market or in the most advantageous market when no principal market
exists. Adjustments to transaction prices or quoted market prices may be required in illiquid or disorderly markets in
order to estimate fair value. Alternative valuation techniques may be appropriate under the circumstances to determine
the value that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction. Market
participants are assumed to be independent, knowledgeable, able and willing to transact an exchange and not acting
under duress. Nonperformance or credit risk is considered in determining the fair value of liabilities. Considerable
judgment may be required in interpreting market data used to develop the estimates of fair value. Accordingly,
estimates of fair value presented herein are not necessarily indicative of the amounts that could be realized in a current
or future market exchange.
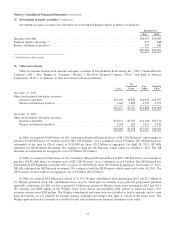
(h) Inventories
Inventories consist of manufactured goods and goods acquired for resale. Manufactured inventory costs include raw
materials, direct and indirect labor and factory overhead. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. As of
December 31, 2012, approximately 38% of our consolidated inventory cost was determined using the last-in-first-out
(“LIFO”) method, 31% using the first-in-first-out (“FIFO”) method, with the remainder using the specific identification
method or average cost methods. With respect to inventories carried at LIFO cost, the aggregate difference in value
between LIFO cost and cost determined under FIFO methods was $793 million and $759 million as of December 31,
2012 and 2011, respectively.
(i) Property, plant and equipment
Additions to property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost. The cost of major additions, improvements and
betterments are capitalized. With respect to constructed assets, all construction related material, direct labor and
contract services as well as certain indirect costs are capitalized. Indirect costs include interest over the construction
period. With respect to constructed assets of certain of our regulated utility and energy subsidiaries that are subject to
authoritative guidance for regulated operations, capitalized costs also include an equity allowance for funds used
during construction, which represents the equity funds necessary to finance the construction of the domestic regulated
facilities. Also see Note 1(p).
Normal repairs and maintenance and other costs that do not improve the property, extend the useful life or otherwise do
not meet capitalization criteria are charged to expense as incurred. Rail grinding costs related to our railroad properties
are expensed as incurred.
Depreciation is provided principally on the straight-line method over estimated useful lives or mandated recovery
periods as prescribed by regulatory authorities. Depreciation of assets of our regulated utilities and railroad is generally
provided using group depreciation methods where rates are based on periodic depreciation studies approved by the
applicable regulator. Under group depreciation, a single depreciation rate is applied to the gross investment in a
particular class of property, despite differences in the service life or salvage value of individual property units within
the same class. When our regulated utilities or railroad retires or sells a component of the assets accounted for using
group depreciation methods, no gain or loss is recognized. Gains or losses on disposals of all other assets are recorded
through earnings.
Our businesses evaluate property, plant and equipment for impairment when events or changes in circumstances
indicate that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable or the assets are being held for sale. Upon the
34