Western Union 2009 Annual Report Download - page 125
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 125 of the 2009 Western Union annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Foreign Currency—Consumer-to-Consumer
The Company’s policy is to use longer-term foreign currency forward contracts, with maturities of up to
36 months at inception and a targeted weighted-average maturity of approximately one year, to mitigate some
of the risk that changes in foreign currency exchange rates compared to the United States dollar could have on
forecasted revenues denominated in other currencies related to its business. At December 31, 2009, the
Company’s longer-term foreign currency forward contracts had maturities of a maximum of 24 months with a
weighted-average maturity of approximately one year. The Company assesses the effectiveness of these foreign
currency forward contracts based on changes in the spot rate of the affected currencies during the period of
designation. Accordingly, all changes in the fair value of the hedges not considered effective or portions of the
hedge that are excluded from the measure of effectiveness are recognized immediately in “Derivative (losses)/
gains, net” within the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income.
The Company also uses short duration foreign currency forward contracts, generally with maturities from
a few days up to one month, to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuations on settlement assets and obligations
between initiation and settlement. In addition, forward contracts, typically with maturities of less than one
year, are utilized to offset foreign exchange rate fluctuations on certain foreign currency denominated cash
positions. None of these contracts are designated as accounting hedges.
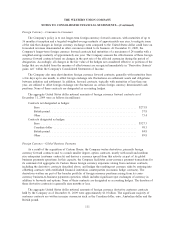
The aggregate United States dollar notional amounts of foreign currency forward contracts as of
December 31, 2009 were as follows (in millions):
Contracts not designated as hedges:
Euro.............................................................. $273.8
British pound ....................................................... 37.8
Other ............................................................. 73.4
Contracts designated as hedges:
Euro.............................................................. $527.3
Canadian dollar ..................................................... 98.3
British pound ....................................................... 84.8
Other ............................................................. 89.8
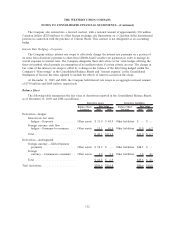
Foreign Currency—Global Business Payments
As a result of the acquisition of Custom House, the Company writes derivatives, primarily foreign
currency forward contracts and, to a much smaller degree, option contracts, mostly with small and medium
size enterprises (customer contracts) and derives a currency spread from this activity as part of its global
business payments operations. In this capacity, the Company facilitates cross-currency payment transactions for
its customers but aggregates its Custom House foreign currency exposures arising from customer contracts,
including the derivative contracts described above, and hedges the resulting net currency risks by entering into
offsetting contracts with established financial institution counterparties (economic hedge contracts). The
derivatives written are part of the broader portfolio of foreign currency positions arising from its cross-
currency business-to-business payments operation, which includes significant spot exchanges of currency in
addition to forwards and options. None of these contracts are designated as accounting hedges. The duration of
these derivative contracts is generally nine months or less.
The aggregate United States dollar notional amounts of foreign currency derivative customer contracts
held by the Company as of December 31, 2009 were approximately $1.0 billion. The significant majority of
customer contracts are written in major currencies such as the Canadian dollar, euro, Australian dollar and the
British pound.
111
THE WESTERN UNION COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)