Travelers 2014 Annual Report Download - page 140
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 140 of the 2014 Travelers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366
 |
 |

Table of Contents
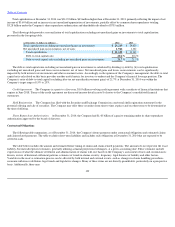
The effect of a particular risk factor on estimates of claim liabilities cannot be isolated in most cases. For example, estimates of potential claim
settlements may be impacted by the risk associated with potential court rulings, but the final settlement agreement typically does not delineate how
much of the settled amount is due to this and other factors.
The evaluation of data is also subject to distortion from extreme events or structural shifts, sometimes in unanticipated ways. For example, the
timing of claims payments in one geographic region will be impacted if claim adjusters are temporarily reassigned from that region to help settle
catastrophe claims in another region.
While some changes in the claim environment are sudden in nature (such as a new court ruling affecting the interpretation of all contracts in
that jurisdiction), others are more evolutionary. Evolutionary changes can occur when multiple factors affect final claim values, with the uncertainty
surrounding each factor being resolved separately, in stepwise fashion. The final impact is not known until all steps have occurred.
Sudden changes generally cause a one
-
time shift in claim liability estimates, although there may be some lag in reliable quantification of their
impact. Evolutionary changes generally cause a series of shifts in claim liability estimates, as each component of the evolutionary change becomes
evident and estimable.
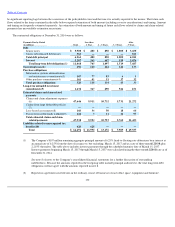
Actuarial methods for analyzing and estimating claims and claim adjustment expense reserves
The principal estimation and analysis methods utilized by the Company's actuaries to evaluate management's existing estimates for prior
accident periods are the paid development method, the case incurred development method, the Bornhuetter
-
Ferguson (BF) method, and average
value analysis combined with the reported claim development method. The BF method is usually utilized for more recent accident periods, with a
transition to other methods as the underlying claim data becomes more voluminous and therefore more credible. These are typically referred to as
conventional actuarial methods. (See Glossary for an explanation of these methods).
While these are the principal methods utilized throughout the Company, actuaries evaluating a particular component for a product line have
available to them the full range of methods developed within the casualty actuarial profession. The Company's actuaries are also continually
monitoring developments within the profession for advances in existing techniques or the creation of new techniques that might improve current
and future estimates.
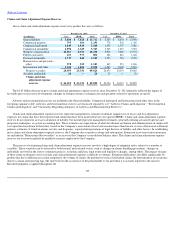
Some components of product line reserves are susceptible to relatively infrequent large claims that can materially impact the total estimate for
that component. In such cases, the Company's actuarial analysis generally isolates and analyzes separately such large claims. The reserves
excluding such large claims are generally analyzed using the conventional methods described above. The reserves associated with large claims are
then analyzed utilizing various methods, such as:
•
Estimating the number of large claims and their average values based on historical trends from prior accident periods, adjusted for
the current environment and supplemented with actual data for the accident year analyzed to the extent available.
•
Utilizing individual claim adjuster estimates of the large claims, combined with continual monitoring of the aggregate accuracy of
such claim adjuster estimates. (This monitoring may lead to supplemental adjustments to the aggregate of such claim estimates.)
•
Utilizing historic longer
-
term average ratios of large claims to small claims, and applying such ratios to the estimated ultimate small
claims from conventional analysis.
•
Ground
-
up analysis of the underlying exposure (typically used for asbestos and environmental).
139
