Singapore Airlines 2016 Annual Report Download - page 134
Download and view the complete annual report
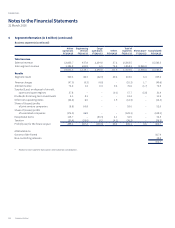
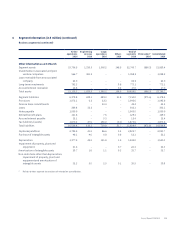
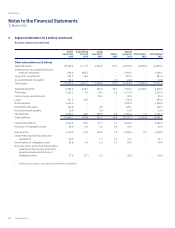
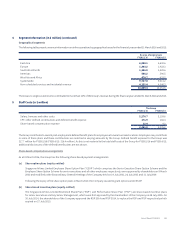
Please find page 134 of the 2016 Singapore Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to the Financial Statements
31 March 2016
2 Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(ac) Employee benefits (continued)
(ii) Defined benefit plans
The net defined benefit liability is the aggregate of the present value of the defined benefit obligation at the end of the reporting
period reduced by the fair value of plan assets (if any).
The cost of providing benefits under the defined benefit plans is determined separately for each plan using the projected unit
credit method.
Defined benefit costs comprise the following:
- Service cost
- Net interest on the net defined benefit liability
- Remeasurements of net defined benefit liability
Service costs which include current service costs, past service costs and gains or losses on non-routine settlements are recognised
as an expense in profit or loss. Past service costs are recognised when a plan amendment or curtailment occurs.
Net interest on the net defined benefit liability is the change during the period in the net defined benefit liability that arises from
the passage of time which is determined by applying the discount rate to the net defined benefit liability. Net interest on the net
defined benefit liability is recognised as an expense in profit or loss.
Remeasurements comprising actuarial gains and losses, and the return on plan assets are recognised immediately in other
comprehensive income in the period in which they arise. All expenses related to the defined benefit plans are recognised as an
expense in profit or loss. Remeasurements are recognised in retained earnings within equity and are not reclassified to profit or
loss in subsequent periods.
Plan assets are assets that are held by long-term employee benefit funds or qualifying insurance policies. Plan assets are not
available to the creditors of the Group, nor can they be paid directly to the Group. The fair value of plan assets is based on market
price information. When no market price is available, the fair value of plan assets is estimated by discounting expected future cash
flows using a discount rate that reflects both the risk associated with the plan assets and the maturity or expected disposal date of
those assets (or, if they have no maturity, the expected period until the settlement of the related obligations).
The Group’s right to be reimbursed of some or all of the expenditure required to settle a defined benefit obligation is recognised as
a separate asset at its fair value when and only when reimbursement is virtually certain.
(iii) Defined contribution plans
As required by law, the companies in Singapore make contributions to the Central Provident Fund scheme in Singapore, a defined
contribution scheme. Certain of the Group’s subsidiary companies and overseas stations outside Singapore make contributions to
their respective countries’ defined contribution pension schemes. Such contributions are recognised as an expense in the period
in which the related service is performed.
(iv) Short-term employee benefits
Short-term employee benefit obligations are measured on an undiscounted basis and are expensed as the related service is
provided. A liability is recognised for the amount expected to be paid under short-term cash bonus or profit-sharing plans if the
Group has a present legal or constructive obligation to pay this amount as a result of past service provided by the employee, and
the obligation can be estimated reliably.
Singapore Airlines132
FINANCIAL