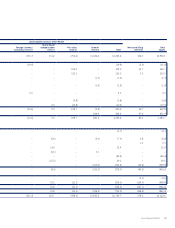
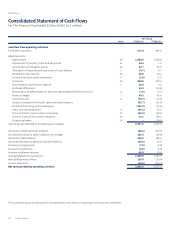
Singapore Airlines 2016 Annual Report Download - page 119
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 119 of the 2016 Singapore Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2 Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(d) Basis of consolidation (continued)
Transactions with non-controlling interests
Non-controlling interests represent the equity in subsidiary companies not attributable, directly or indirectly, to owners of the Parent,
and are presented separately in the consolidated statement of comprehensive income and within equity in the consolidated statement
of financial position, separately from equity attributable to owners of the Parent.
Changes in the Company’s ownership interest in a subsidiary company that do not result in a loss of control are accounted for as equity
transactions. In such circumstances, the carrying amounts of the controlling and non-controlling interests are adjusted to reflect the
changes in their relative interests in the subsidiary company. Any dierence between the amount by which the non-controlling interest
is adjusted and the fair value of the consideration paid or received is recognised directly in equity and attributed to owners of the Parent.
Adjustments to non-controlling interests arising from transactions that do not involve the loss of control are based on a proportionate
amount of the net assets of the subsidiary companies.
(e) Subsidiary, associated and joint venture companies
In the Company’s separate financial statements, investments in subsidiary and associated companies are accounted for at cost less
accumulated impairment losses.
A subsidiary company is an investee that is controlled by the Group. The Group controls an investee when it is exposed, or has rights, to
variable returns from its involvement with the investee and has the ability to aect those returns through its power over the investee. The
financial statements of subsidiary companies are included in the consolidated financial statements from the date the control commences
until the date the control ceases.
The Group reassesses whether or not it controls an investee if facts and circumstances indicate that there are changes to one or more of
the elements of control listed above.
The accounting policies of subsidiary companies have been changed when necessary to align them with policies adopted by the Group.
Losses applicable to the non-controlling interests in a subsidiary company are allocated to the non-controlling interests even if doing so
causes the non-controlling interest to have a deficit balance.
An associated company is an entity in which the Group has significant influence, but not control or joint control, over the financial and
operating policies of the entity. Significant influence is presumed to exist when the Group holds 20% or more of the voting power of
another entity. A list of the Group’s associated companies is shown in Note 24 to the financial statements.
A joint venture company is an arrangement in which the Group has joint control, whereby the Group has rights to the net assets of the
arrangement, rather than rights to its assets and obligations for its liabilities. A list of the Group’s joint venture companies is shown in
Note 25 to the financial statements.
The Group accounts for its investments in associated and joint venture companies using the equity method from the date on which it
becomes an associated or joint venture company.
On acquisition of the investment, any excess of the cost of the investment over the Group’s share of the net fair value of the investee’s
identifiable assets and liabilities is accounted for as goodwill and is included in the carrying amount of the investment. Any excess of the
Group’s share of the net fair value of the investee’s identifiable assets and liabilities over the cost of the investment is included as income
in the determination of the entity’s share of the associated or joint venture company’s profit or loss in the period in which the investment
is acquired.
Annual Report FY2015/16 117