Time Warner Cable 2009 Annual Report Download - page 88
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 88 of the 2009 Time Warner Cable annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Maturities
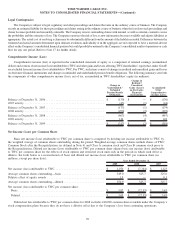
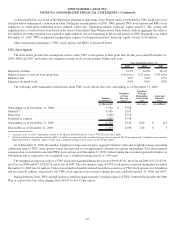
Annual maturities of long-term debt and mandatorily redeemable preferred equity total $0 in 2010, $1.261 billion in 2011,
$2.109 billion in 2012, $1.800 billion in 2013, $1.751 billion in 2014 and $15.751 billion thereafter.
Fair Value of Debt
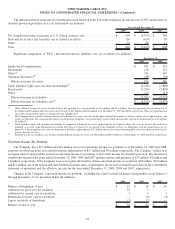
Based on the level of interest rates prevailing at December 31, 2009 and 2008, the fair value of TWC’s fixed-rate debt and the TW
NY Cable Preferred Membership Units exceeded the carrying value by approximately $2.268 billion as of December 31, 2009, and the
carrying value exceeded the fair value by approximately $540 million as of December 31, 2008. Unrealized gains or losses on debt do not
result in the realization or expenditure of cash and are not recognized for financial reporting purposes unless the debt is retired prior to its
maturity.
Interest Rate Risk
The Company is exposed to the market risk of adverse changes in interest rates. To manage the volatility relating to these exposures,
the Company’s policy is to maintain a mix of fixed-rate and variable-rate debt by entering into various interest rate derivative transactions
as described below to help achieve that mix. Using interest rate swaps, the Company agrees to exchange, at specified intervals, the
difference between fixed and variable interest amounts calculated by reference to an agreed-upon notional principal amount.
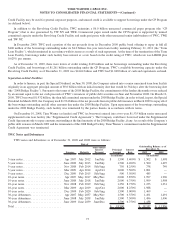
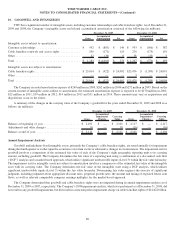
The following table summarizes the terms of the Company’s existing fixed to variable interest rate swaps as of December 31, 2009:
Maturities ................................................................................ 2012-2015
Notional amount (in millions) ................................................................. $ 5,250
Average pay rate (variable based on LIBOR plus variable margins) ...................................... 4.03%
Average receive rate (fixed) ................................................................... 6.24%
Estimated fair value (in millions) ............................................................... $ (12)
The notional amounts of interest rate instruments, as presented in the above table, are used to measure interest to be paid or received
and do not represent the amount of exposure to credit loss. Interest rate swaps represent an integral part of the Company’s interest rate risk
management program, with a benefit to interest expense, net, in 2009 of $30 million.
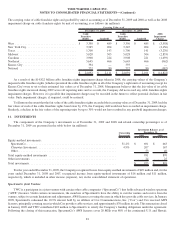
8. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Company has entered into the following derivative contracts, which have been designated as either fair value hedges or cash
flow hedges, in order to hedge certain identified risks:
Interest rate swap contracts – Interest rate swap contracts (“interest rate swaps”) are used to change the nature of outstanding debt
(i.e., convert fixed-rate debt into variable-rate debt or convert variable-rate debt into fixed-rate debt). As of December 31, 2009, the
Company had outstanding interest rate swap contracts that convert $5.250 billion of fixed-rate debt to variable-rate debt. Such contracts
have been designated as fair value hedges.
Interest rate lock contracts – Interest rate lock contracts (“interest rate locks”) are used to mitigate the risk to the Company from
changes in interest rates during the period leading up to the issuance of fixed-rate debt. As of December 31, 2009, the Company had no
outstanding interest rate lock contracts; however, contracts entered into previously by the Company have been designated as cash flow
hedges.
Foreign currency forward contracts – Foreign currency forward contracts (“forward contracts”) are used to mitigate the risk to the
Company from changes in foreign currency exchange rates. The Company currently has exposure to changes in U.S. Dollar – Philippine
peso exchange rates related to certain overseas call center operations. As of December 31, 2009, the Company had outstanding foreign
currency forward contracts to buy Philippine pesos for $30 million. These contracts have been designated as cash flow hedges.
In addition to the above derivative financial instruments that have been designated as either fair value hedges or cash flow hedges,
the Company’s equity award reimbursement liability to Time Warner is accounted for as a derivative financial instrument not designated
as a hedging instrument.
76
TIME WARNER CABLE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)