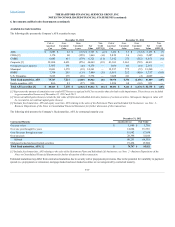
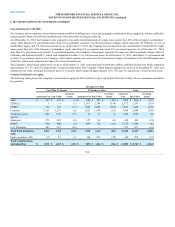
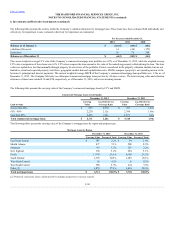
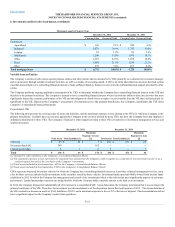
The Hartford 2012 Annual Report Download - page 195
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 195 of the 2012 The Hartford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
The Company utilizes a variety of over-the-counter and exchange traded derivative instruments as a part of its overall risk management strategy, as well as to
enter into replication transactions. Derivative instruments are used to manage risk associated with interest rate, equity market, credit spread, issuer default,
price, and currency exchange rate risk or volatility. Replication transactions are used as an economical means to synthetically replicate the characteristics and
performance of assets that would be permissible investments under the Company's investment policies. The Company also purchases and issues financial
instruments and products that either are accounted for as free-standing derivatives, such as certain reinsurance contracts, or may contain features that are
deemed to be embedded derivative instruments, such as the GMWB rider included with certain variable annuity products.
Certain derivatives the Company enters into satisfy the hedge accounting requirements as outlined in Note 1 of these financial statements. Typically, these
hedge relationships include interest rate and foreign currency swaps where the terms or expected cash flows of the securities closely match the “pay” leg terms
of the swap. The swaps are typically used to manage interest rate duration of certain fixed maturity securities, or liability contracts, or convert securities, or
liabilities, denominated in a foreign currency to US dollars. The hedge strategies by hedge accounting designation include:
Cash flow hedges
Interest rate swaps are predominantly used to manage portfolio duration and better match cash receipts from assets with cash disbursements required to fund
liabilities. These derivatives convert interest receipts on floating-rate fixed maturity securities or interest payments on floating-rate guaranteed investment
contracts to fixed rates. The Company also enters into forward starting swap agreements primarily to hedge interest rate risk inherent in the assumptions used
to price certain liabilities.
Foreign currency swaps are used to convert foreign currency-denominated cash flows related to certain investment receipts and liability payments to U.S.
dollars in order to reduce cash flow fluctuations due to changes in currency rates.
Fair value hedges
Interest rate swaps are used to hedge the changes in fair value of certain fixed rate liabilities and fixed maturity securities due to fluctuations in interest rates.
Foreign currency swaps are used to hedge the changes in fair value of certain foreign currency-denominated fixed rate liabilities due to changes in foreign
currency rates by swapping the fixed foreign payments to floating rate U.S. dollar denominated payments.
Derivative relationships that do not qualify for hedge accounting or “non-qualifying strategies” primarily include the hedge programs for our U.S. and
international variable annuity products, as well as the hedging and replication strategies through the use of credit default swaps. In addition, hedges of interest
rate and foreign currency risk of certain fixed maturities and liabilities do not qualify for hedge accounting. These non-qualifying strategies include:
Interest rate swaps, swaptions, caps, floors, and futures
The Company uses interest rate swaps, swaptions, caps, floors, and futures to manage duration between assets and liabilities in certain investment portfolios.
In addition, the Company enters into interest rate swaps to terminate existing swaps, thereby offsetting the changes in value of the original swap. As of
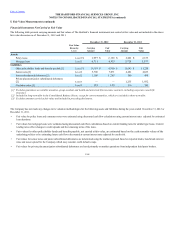
December 31, 2012 and 2011, the notional amount of interest rate swaps in offsetting relationships was $ 7.5 billion and $7.8 billion, respectively.
Foreign currency swaps and forwards
The Company enters into foreign currency swaps and forwards to convert the foreign currency exposures of certain foreign currency-denominated fixed
maturity investments to U.S. dollars.
Japan 3Win foreign currency swaps
Prior to the second quarter of 2009, the Company offered a yen denominated fixed annuity product through a wholly-owned Japanese subsidiary and reinsured
to a wholly-owned U.S. subsidiary. The U.S. subsidiary invests in U.S. dollar denominated securities to support the yen denominated fixed liability
payments and entered into currency rate swaps to hedge the foreign currency exchange rate and yen interest rate exposures that exist as a result of U.S. dollar
assets backing the yen denominated liability.
F-53