Sara Lee 2009 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2009 Sara Lee annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to financial statements
Dollars in millions except per share data
74 Sara Lee Corporation and Subsidiaries
SFAS 157 defines fair value as the price that would be received
to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability (i.e., exit price) in an
orderly transaction between market participants at the measure-
ment date. SFAS 157 requires disclosures that categorize assets
and liabilities measured at fair value into one of three different lev-
els depending on the assumptions (i.e., inputs) used in the
valuation. Level 1 provides the most reliable measure of fair value
while level 3 generally requires significant management judgment.
Financial assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based
on the lowest level of input significant to the fair value measure-
ment. The SFAS 157 fair value hierarchy is defined as follows:
Level 1 – Unadjusted Quoted Prices
Valuations are based on
unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or
liabilities. An example would be a marketable equity security that
is traded on a major stock exchange.
Level 2 – Pricing Models with Significant Observable Inputs
Valuations are based on information derived from either an active
market quoted price, which may require further adjustment based
on the attributes of the financial asset or liability being measured,
or an inactive market transaction. Circumstances when adjustments
to market quoted prices may be appropriate include (i) a quoted
price for an actively traded equity investment that is adjusted for
a contractual trading restriction, or (ii) the fair value derived from
a trade of an identical or similar security in an inactive market. An
interest rate swap derivative valued based on a LIBOR swap curve
is an example of a level 2 asset or liability.
Level 3 – Pricing Models with Significant Unobservable Inputs
Valuations are based on internally derived assumptions surrounding
the timing and amount of expected cash flows for the financial
instrument, which are significant to the overall fair value measure-
ment. These assumptions are unobservable in either an active or
inactive market. The inputs reflect management’s best estimate of
what market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability
at the measurement date. A goodwill impairment test that utilizes
an internally developed discounted cash flow model is an example
of a level 3 asset or liability.
Effective the beginning of fiscal 2009, the corporation implemented
SFAS 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial
Liabilities” (SFAS 159), which allows companies the option to report
selected financial assets and financial liabilities at fair value. The
adoption of SFAS 159 had no impact on the consolidated financial
statements as the corporation did not elect the fair value option.
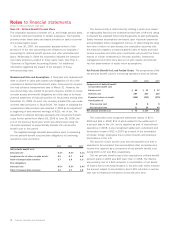
The carrying amounts of cash and equivalents, trade accounts
receivables, accounts payable, derivative instruments and notes
payable approximate fair values.
The fair values and carrying amounts of long-term debt, including
the current portion, at June 27, 2009 was $2,796 and $2,800 and
at June 28, 2008 was $2,929 and $2,908 respectively.
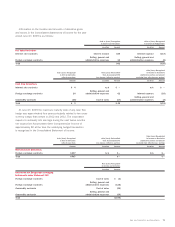
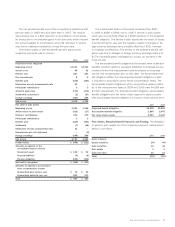
Information on the location and amounts of derivative fair values
in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet at June 27, 2009
and June 28, 2008 is as follows:
Other Other Accrued Other
Current Assets Non-Current Assets Liabilities – Other Non-Current Liabilities
2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008
Derivatives designated as hedging
instruments under Statement 133
Interest rate contracts2$÷3 $÷1 $30 $9 $÷– $÷– $÷÷– $÷÷–
Foreign exchange contracts21– –– 83249308
Commodity contracts111 –– –– ––
Total derivatives designated as hedges 5 2 30 9 8 3 249 308
Derivatives not designated as hedging
instruments under Statement 133
Foreign exchange contracts267 38 – – 44 31 – –
Commodity contracts1132––––––
Total derivatives not designated as hedges 68 70 – – 44 31 – –
Total derivatives $73 $72 $30 $9 $52 $34 $249 $308
1Categorized as level 1: Fair value of level 1 assets and liabilities as of June 27, 2009 are $2 and $0 and June 28, 2008 are $33 and $0, respectively.
2 Categorized as level 2: Fair value of level 2 assets and liabilities as of June 27, 2009 are $101 and $301 and June 28, 2008 are $48 and $342, respectively.