Sara Lee 2009 Annual Report Download - page 74
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 74 of the 2009 Sara Lee annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to financial statements
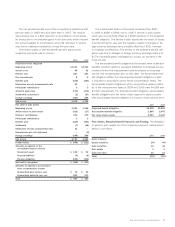
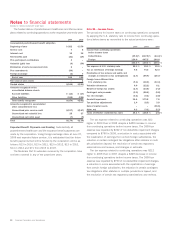
Dollars in millions except per share data
Fair Value Hedge A hedge of a recognized asset or liability or an
unrecognized firm commitment is declared as a fair value hedge
which qualify for hedge accounting. For fair value hedges, both the
effective and ineffective portions of the changes in the fair value of
the derivative, along with the gain or loss on the hedged item that
is attributable to the hedged risk, are recorded in earnings and are
reported in the Consolidated Statements of Income on the same
line as the hedged item.
Cash Flow Hedge A hedge of a forecasted transaction, firm
commitment or of the variability of cash flows to be received or
paid related to a recognized asset or liability is declared a cash
flow hedge. Cash flow hedges qualify for hedge accounting. The
effective portion of the change in the fair value of the derivative
that is declared as a cash flow hedge is recorded in accumulated
other comprehensive income (within common stockholders’ equity)
and later reclassified to the income statement at the same time
the underlying hedged item impacts the income statement. In addi-
tion, both the fair value of changes excluded from the corporation’s
effectiveness assessments and the ineffective portion of the
changes in the fair value of derivatives used as cash flow hedges
are reported in “Selling, general and administrative expenses”
line in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Net Investment Hedge A hedge of the exposure of changes in the
underlying foreign currency denominated subsidiary net assets is
declared as a net investment hedge. Net investment hedges qualify
for hedge accounting. Net investment hedges can include either
derivative or non-derivative instruments including non-U.S. dollar
financing transactions or non-U.S. dollar assets or liabilities, includ-
ing intercompany loans. The effective portion of the change in the
fair value of net investment hedges is recorded in the cumulative
translation adjustment account within common stockholders’ equity.
At June 27, 2009 the U.S. dollar equivalent of intercompany loans
designated as net investment hedges was $3.2 billion.
Mark-to-Market Hedge A derivative that is not qualified for hedge
accounting in one of the categories above is accounted for under
mark-to-market accounting and referred to as a mark-to-market
hedge. Changes in the fair value of a mark-to-market hedge are
recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Income to act as an
economic hedge against the changes in the values of another item
or transaction. Changes in the fair value of derivatives classified as
mark-to-market hedges are reported in earnings in either the “Cost
of sales” or “Selling, general and administrative expenses” lines of
the Consolidated Statements of Income where the change in value
of the underlying transaction is recorded.
Types of Derivative Instruments
Interest Rate and Cross Currency Swaps
To manage interest rate
risk, the corporation has entered into interest rate swaps that effec-
tively convert certain fixed-rate debt instruments into floating-rate
debt instruments. Interest rate swap agreements that are effective
at hedging the fair value of fixed-rate debt agreements are designated
and accounted for as fair value hedges. The corporation utilizes
interest rate swap derivatives in order to maintain a targeted amount
of both fixed-rate and floating-rate long term debt and notes payable.
Currently the corporation has a fixed interest rate on approximately
70% of long-term debt and notes payable issued.
The corporation has issued certain foreign-denominated debt
instruments and utilizes cross currency swaps to reduce the variabil-
ity of functional currency cash flows related to the foreign currency
debt. Cross currency swap agreements that are effective at hedging
the variability of foreign-denominated cash flows are designated
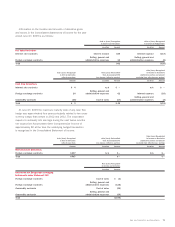
and accounted for as cash flow hedges. As of June 27, 2009, the
total notional amount of the corporation’s interest rate swaps and
cross currency swaps were $385 and $786, respectively.
In 2009, in connection with the funding of the anticipated
retirement of the 6.25% notes in September 2011, the corporation
executed a $50 forward starting swap to effectively fix the cash flows
related to interest payments on the anticipated debt issuance.
Currency Forward Exchange, Futures and Option Contracts
The
corporation uses forward exchange and option contracts to reduce
the effect of fluctuating foreign currencies on short-term foreign-
currency-denominated intercompany transactions, third-party product-
sourcing transactions, foreign-denominated investments and other
known foreign currency exposures. Gains and losses on the deriva-
tive instruments are intended to offset losses and gains on the
hedged transaction in an effort to reduce the earnings volatility
resulting from fluctuating foreign currency exchange rates. Forward
currency exchange contracts mature at the anticipated cash require-
ment date of the hedged transaction, generally within one year to
eighteen months. Forward currency exchange contracts which are
effective at hedging the fair value of a recognized asset or liability
are designated and accounted for as fair value hedges. All remain-
ing currency forward and options contracts are accounted for as
mark-to-market hedges.
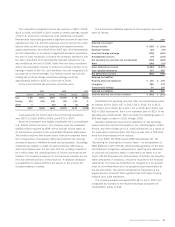
The principal currencies hedged by the corporation include the
European euro, British pound, Danish krone, Hungarian forint, U.S.
dollar, Swiss franc and Australian dollar. As of June 27, 2009, the
net U.S. dollar equivalent of commitments to purchase and sell
foreign currencies is $2,374 and $2,347, respectively, using the
exchange rate at the reporting date. The corporation hedges virtually
all foreign exchange risk derived from recorded transactions and firm
commitments and only hedges foreign exchange risk related to antic-
ipated transactions where the exposure is potentially significant.
72 Sara Lee Corporation and Subsidiaries