PG&E 2009 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
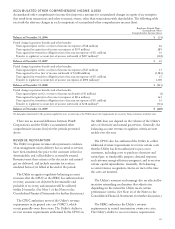
Please find page 76 of the 2009 PG&E annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Corporation’s Consolidated Statements of Income as a
non-operating expense or income (in Other income
(expense), net). (See Notes 10 and 11 of the Notes to the
Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of
these instruments.)
On January 13, 2009, PG&E Corporation, upon request
by an investor, converted $28 million of Convertible
Subordinated Notes into 1,855,865 shares, at the
conversion price of $15.09 per share. Additionally, on
July 1, 2009, PG&E Corporation, upon request by an
investor, converted $5 million of Convertible
Subordinated Notes into 331,404 shares, at the conversion
price of $15.09 per share.
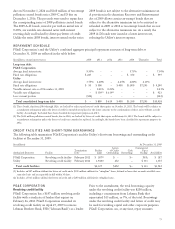
UTILITY
Senior Notes
At December 31, 2009, the Utility had outstanding $8.6
billion of senior notes with various interest rates and
maturity dates, including the following issuances made
during 2009.
On March 6, 2009, the Utility issued $550 million
principal amount of 6.25% Senior Notes due March 1,
2039.
On June 11, 2009, the Utility issued $500 million
principal amount of Floating Rate Senior Notes due
June 10, 2010. The interest rate for the Floating Rate Senior
Notes is equal to the three-month London Interbank
Offered Rate plus 0.95% and resets quarterly. At
December 31, 2009, the interest rate on the Floating Rate
Senior Notes was 1.21%.
On November 18, 2009, the Utility issued $550 million
principal amount of 5.40% Senior Notes due January 15,
2040.
The Utility’s senior notes are unsecured and rank
equally with the Utility’s other senior unsecured and
unsubordinated debt. Under the indenture for the senior
notes, the Utility has agreed that it will not incur secured
debt or engage in sales leaseback transactions (except for
(1) debt secured by specified liens, and (2) aggregate other
secured debt and sales and leaseback transactions not
exceeding 10% of the Utility’s net tangible assets, as
defined in the indenture) unless the Utility provides that
the senior notes will be equally and ratably secured.
Pollution Control Bonds
The California Pollution Control Financing Authority and
the California Infrastructure and Economic Development
Bank have issued various series of tax-exempt pollution
control bonds for the benefit of the Utility. Under the
pollution control bond loan agreements related to the
Series 1996 A bonds, the Series 2004 A–D bonds, and the
Series 2008 F and G bonds, the Utility is obligated to pay
on the due dates an amount equal to the principal;
premium, if any; and interest on these bonds to the
trustees for these bonds. With respect to the Series 1996 C,
E, and F bonds; the Series 1997 B bonds; and the Series
2009 A–D bonds, the Utility reimburses the letter of credit
providers for their payments to the trustee for these bonds,
or if a letter of credit provider fails to pay under its
respective letter of credit, the Utility is obligated to pay the
principal; premium, if any; and interest on those bonds.
All payments on the Series 1996 C, E, and F bonds; the
Series 1997 B bonds; and the Series 2009 A–D bonds are
made through draws on separate direct-pay letters of credit
for each series issued by a financial institution.
All of the pollution control bonds were used to finance
or refinance pollution control facilities at the Geysers
geothermal power plant or at the Utility’s Diablo Canyon
nuclear power plant and were issued as “exempt facility
bonds” within the meaning of Section 142(a) of the
Internal Revenue Code of 1954, as amended (“Code”). The
Utility agrees not to take any action or fail to take any
action if any such action or inaction would cause the
interest on the bonds to be taxable or to be other than
exempt facility bonds.
In 1999, the Utility sold the Geysers geothermal power
plant to Geysers Power Company, LLC pursuant to
purchase and sale agreements stating that Geysers Power
Company, LLC will use the bond-financed facilities solely
as pollution control facilities within the meaning of
Section 103(b)(4)(F) of the Code. Although Geysers Power
Company, LLC subsequently filed a petition for
reorganization under Chapter 11, it assumed the purchase
and sale agreements under its Chapter 11 plan of
reorganization that became effective on January 31, 2008.
The Utility has no knowledge that Geysers Power
Company, LLC intends to cease using the bond-financed
facilities solely as pollution control bonds facilities within
the meaning of Section 103(b)(4)(F) of the Code.
The Utility has obtained credit support from insurance
companies for the Series 1996 A bonds and the Series 2004
A–D bonds such that if the Utility does not pay the
principal and interest on any series of these insured bonds,
the bond insurer for that series will pay the principal and
interest.
On September 1, 2009, the California Infrastructure and
Economic Development Bank issued $149 million of
tax-exempt pollution control bonds series 2009 A and B
72