PG&E 2009 Annual Report Download - page 102
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 102 of the 2009 PG&E annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. PG&E
Corporation’s and the Utility’s investment policies and
strategies are designed to increase the ratio of trust assets to
plan liabilities at an acceptable level of funded status
volatility.
Interest rate risk and equity risk are the key determinants
of PG&E Corporation’s and the Utility’s funded status
volatility. In addition to affecting the trust’s fixed income
portfolio market values, interest rate changes also influence
liability valuations as discount rates move with current
bond yields. To manage this risk, PG&E Corporation’s and
the Utility’s trusts hold significant allocations to fixed
income investments that include U.S. government
securities, corporate securities, and other fixed income
securities. Although they contribute to funded status
volatility, equity investments are held to reduce long-term
funding costs due to their higher expected return. The
equity investment allocation is implemented through
diversified U.S., non-U.S., and global portfolios that
include common stock and commingled funds across
multiple industry sectors. Absolute return investments
include hedge fund portfolios that are managed to diversify
the plan’s holdings in equity and fixed income investments
by exhibiting returns with low correlation to the direction
of these markets. Over the last three years, target
allocations to equity investments have generally declined in
favor of longer-maturity fixed income investments as a
means of dampening future funded status volatility.
PG&E Corporation and the Utility apply a risk
management framework for managing the risks associated
with employee benefit plan trust assets. The guiding
principles of this risk management framework are the clear
articulation of roles and responsibilities, appropriate
delegation of authority, and proper accountability and
documentation. Trust investment policies and investment
manager guidelines include provisions to ensure prudent
diversification, manage risk through appropriate use of
physical direct asset holdings and derivative securities, and
identify permitted and prohibited investments.
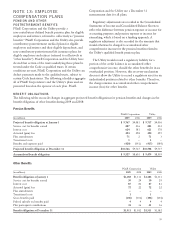
The target asset allocation percentages for major categories of trust assets for pension and other benefit plans at
December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 are as follows:
Pension Benefits Other Benefits
2010 2009 2008 2010 2009 2008
U.S. Equity 26% 32% 31% 26% 37% 35%
Non-U.S. Equity 14% 18% 17% 13% 18% 16%
Global Equity 5% 5% 3% 3% 3% 2%
Absolute Return 5% 5% 4% 3% 3% 3%
Fixed Income 50% 40% 42% 54% 34% 34%
Cash Equivalents 0% 0% 3% 1% 5% 10%
Total 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100%
Equity securities include a small amount (less than 0.1%
of total plan assets) of PG&E Corporation common stock.
The maturity of fixed income securities at December 31,
2009 ranged from less than one year to 88 years and the
average duration of the bond portfolio was approximately
10.6 years. The maturity of fixed income securities at
December 31, 2008 ranged from zero to 59 years and the
average duration of the bond portfolio was approximately
12.2 years.
98