Motorola 2010 Annual Report Download - page 117
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 117 of the 2010 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
109
Not all of the standard inputs listed will be used each time in the valuation models. For each asset class, quantifiable
inputs related to perceived market movements and sector news may be considered in addition to the standard
inputs.
In determining the fair value of the Company’s foreign currency derivatives, the Company uses forward
contract and option valuation models employing market observable inputs, such as spot currency rates, time value
and option volatilities. Since the Company primarily uses observable inputs in its valuation of its derivative assets
and liabilities, they are classified as Level 2 assets.
Level 3—Fixed income securities are debt securities that do not have actively traded quotes as of the financial
statement date. Determining the fair value of these securities requires the use of unobservable inputs, such as
indicative quotes from dealers, extrapolated data, proprietary models and qualitative input from investment
advisors. As such, these securities are classified within Level 3.
At December 31, 2010, the Company has $1.0 billion of investments in money market mutual funds classified
as Cash and cash equivalents in its consolidated balance sheet. The money market funds have quoted market prices
that are generally equivalent to par.
10. Long-term Customer Financing and Sales of Receivables
Long-term Customer Financing
Long-term receivables consist of trade receivables with payment terms greater than twelve months, long-term
loans and lease receivables under sales-type leases. Long-term receivables consist of the following:
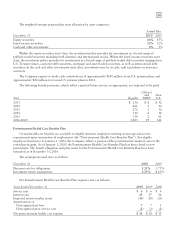
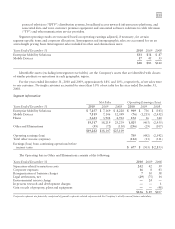
December 31 2010 2009
Long-term receivables $286 $154
Less allowance for losses (3) (9)
283 145
Less current portion (21) (28)
Non-current long-term receivables, net $262 $117
The current portion of long-term receivables is included in Accounts receivable and the non-current portion of
long-term receivables is included in Other assets in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets. Interest income
recognized on long-term receivables for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 was $14 million,
$2 million and $3 million, respectively.
Certain purchasers of the Company’s infrastructure equipment may request that the Company provide long-
term financing (defined as financing with a term of greater than one year) in connection with the sale of equipment.
These requests may include all or a portion of the purchase price of the equipment. The Company’s obligation to
provide long-term financing may be conditioned on the issuance of a letter of credit in favor of the Company by a
reputable bank to support the purchaser’s credit or a pre-existing commitment from a reputable bank to purchase
the long-term receivables from the Company. The Company had outstanding commitments to provide long-term
financing to third parties totaling $356 million at December 31, 2010, compared to $406 million at December 31,
2009. Of these amounts, $27 million was supported by letters of credit or by bank commitments to purchase long-
term receivables at December 31, 2010, compared to $13 million supported at December 31, 2009. The majority of
the outstanding commitments at December 31, 2010 are to a small number of network operators in the Middle East
region. The Company will retain the funded portion of the financing arrangements related to the Networks segment
following the sale to NSN, which totaled approximately $235 million at December 31, 2010.
In addition to providing direct financing to certain equipment customers, the Company also assists customers in
obtaining financing directly from banks and other sources to fund equipment purchases. The Company had
committed to provide financial guarantees relating to customer financing totaling $13 million at December 31,
2010, compared to $31 million at December 31, 2009 (including $9 million and $27 million at December 31, 2010
and 2009, respectively, relating to the sale of short-term receivables). Customer financing guarantees outstanding
were $4 million at both December 31, 2010 and 2009 (including $2 million at both December 31, 2010 and 2009,
relating to the sale of short-term receivables).