Aflac 2006 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2006 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
32
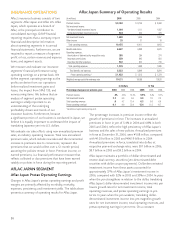
In June 2006, we began selling a new cancer plan aimed at
existing cancer insurance policyholders. This new product
provides additional benefits for inpatient and outpatient care.
Our cancer life policies are also marketed by Dai-ichi Mutual
Life and in June 2006, Dai-ichi Life began selling a new cancer
product customized for their market. As a result, new sales
from cancer insurance products were stable in 2006. We are
convinced that the affordable cancer products Aflac Japan
provides will continue to be an important part of our product
portfolio.
We continue to expect 2007 to be a challenging year from a
sales perspective and look for sales to again decline in the first
half of the year, followed by modest sales increases in the
second half of 2007.
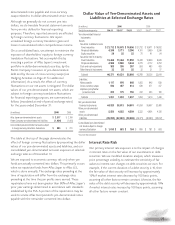
Aflac Japan Investments
Growth of investment income in yen is affected by available
cash flow from operations, timing of and yields on new
investments, and the effect of yen/dollar exchange rates on
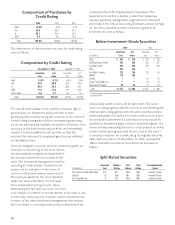
dollar-denominated investment income. Aflac Japan has
invested in privately issued securities to secure higher yields
than Japanese government or other public corporate bonds
would have provided, while still adhering to prudent standards
for credit quality. All of our privately issued securities are rated
investment grade at the time of purchase. These securities are
generally issued with standard documentation for medium-
term note programs and have appropriate covenants.
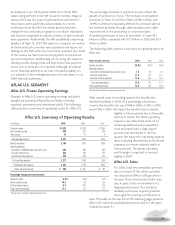
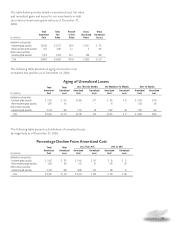
The following table presents the results of Aflac Japan’s
investment activities for the years ended December 31.
At December 31, 2006, the yield on Aflac Japan’s investment
portfolio, including dollar-denominated investments, was
4.14%, compared with 4.22% a year ago. See Investments and
Cash on Page 36 for additional information.
Japanese Economy
Recent events indicate that Japan’s economy has begun to
recover. The Bank of Japan’s January 2007 Monthly Report of
Recent Economic & Financial Developments stated that
Japan’s economy is expanding moderately, noting increases in
exports and capital expenditures and moderate increases in
household income, private consumption and housing
investment, all against the backdrop of high corporate profits
and expansion of overseas economies. The report did note a
downward trend related to public investment and projected
the trend to continue. However, it also included an
expectation that the economy would continue to expand
moderately, supported by expectations of increasing exports
and domestic private demand. Nevertheless, the time required
for a full economic recovery remains uncertain.
Japan’s system of compulsory public health care insurance
provides medical coverage to every Japanese citizen. These
public medical expenditures are covered by a combination of
premiums paid by insureds and their employers, taxes, and
copayments from the people who receive medical service.
However, given Japan’s aging population, the resources
available to these publicly funded social insurance programs
have come under increasing pressure. As a result, copayments
and other out-of-pocket expenses have been rising and
affecting more people. In 2003, copayments were raised from
20% to 30% for most consumers and other reforms were
implemented in 2006. Additional reforms are being
considered. We believe higher out-of-pocket expenses will
lead more consumers to purchase supplemental insurance
plans. Many insurance companies have recognized the
opportunities for selling supplemental medical insurance in
Japan and have launched new products in recent years.
However, we believe our favorable cost structure compared
with other insurers makes us a very effective competitor. In
addition, we believe our brand, customer service, and financial
strength also benefit our market position.
Japanese Regulatory Environment
The FSA adopted new mortality tables effective April 1, 2007,
that will be used when developing our policy premium and
reserving assumptions on newly underwritten policies. These
new tables reflect recent improvements in survival rates in
Japan. If our other assumptions remain unchanged, these
revisions will generally lead to a decrease in policy premiums
for death benefit products and an increase in premium rates
for third sector products and annuities.
Additionally, the FSA has implemented a new rule for third
sector product reserving. The new reserving rule will be
implemented in the Japanese fiscal year starting April 1, 2007.
Under the new rule, we are required to conduct stress testing
of our reserves using a prescribed method that incorporates
actual incidence rates. The results of the tests and their
relation to our reserves determine whether reserve
strengthening is required. We do not anticipate that the new
reserving requirements will have a material impact on our
FSA-based financial statements or our pricing.
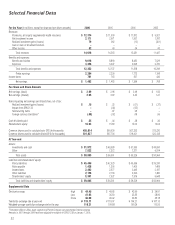
2006 2005 2004
New money yield - yen only 3.10% 2.95% 2.94%
New money yield - blended 3.33 3.19 3.13
Return on average invested assets,
net of investment expenses 4.11 4.14 4.26