Ubisoft 2006 Annual Report Download - page 75
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 75 of the 2006 Ubisoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
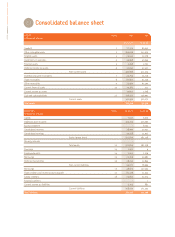
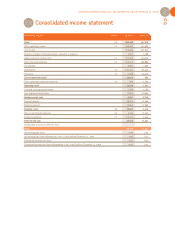
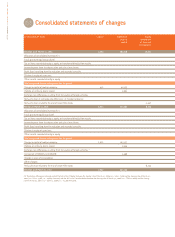
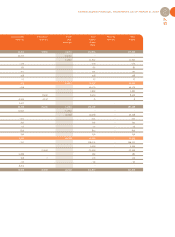
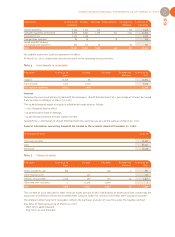
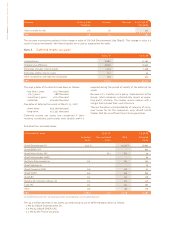
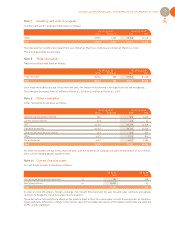
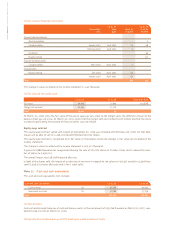
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF MARCH 31, 2007
63
2
• Share-based payments
Stock option plans allow the Group’s staff members to pur-
chase the company’s shares. The fair value of the options
granted is recognized in wages and social security costs as
an offset of an increase in equity. The fair value is measu-
red at the grant date and spread out over the entire ves-
ting period. The fair value of the options is measured using
a binomial model based on the terms and conditions of the
options defined at the grant date:
stock option plans: this compensation is recorded in the
income statement and spread out over the vesting
period; however, the straight-line method is not used, in
accordance with the vesting terms defined in Ubisoft’s
plan rules;
group savings plan: the accounting expense is equal to
the discount granted to employees, i.e., the difference
between the share subscription price and the share price
at the grant date. This expense is recorded immediately
as of the plan subscription date.
• Individual right to training
France's law of May 4, 2004, grants French employees an
individual right to training. Under this law, employees may
receive training at their initiative, with their employer's
approval.
Full-time employees acquire a right to between 20 and 21
hours of training each year, in accordance with the labor
agreements applicable within each firm.
The rights acquired annually may be accrued for up to six
years.
The assumption made at March 31, 2007 for recognition of
these rights is:
15% of the valuation of the hours acquired at March 31,
2007 (with social security taxes) of companies that are
members of FAFIEC (organization that provides professio-
nal training) are recorded as a provision.
Provisions
A provision is recorded when:
the company has a current obligation (legal or implicit)
resulting from a past event;
it is probable that an outflow of resources representing
economic benefits will be required to settle the obliga-
tion;
the amount of the obligation can be measured reliably.
If these conditions are not met, no provision is recorded.
When the effect of the time value is material, the provision
amount is determined by discounting expected future cash
flows using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects the cur-
rent market assessments of the time value of money and,
where appropriate, the risks specific to the liability.
Trade creditors and related accounts payable
Trade creditors and related accounts are valued at amorti-
zed cost.
Sales
Proceeds from the sale of goods are recognized in the
income statement when the significant risks and benefits
inherent to ownership of the goods have been transferred
to the purchaser.
All sales are measured at the fair value of the considera-
tion received or to be received, less rebates, reductions,
trade, volume and financial discounts and provisions for
returned merchandise.
Current operating result
Current operating result includes gross margin, adminis-
trative and commercial expenses, pension and retirement
costs, and the cost of share-based payments.
Other operating income and expenses
Other operating income and expenses are items that are
few in number and correspond to infrequent events.
Financing costs and other financial income and
expenses
Financial result consists of the cost of net borrowings and
other financial income and expenses.
The cost of net borrowings includes:
income from cash and cash equivalents, which includes
profit on sales of investment securities, interest income
and the impact of hedging operations,
the cost of gross borrowings, which includes all interest
charges on financing transactions.
Other financial income and expenses include income on
sales of non-consolidated securities, changes in fair value
of financial instruments (assets, liabilities and derivatives),
foreign exchange results and other financial income and
expenses.
Income taxes
Income tax (income or expense) includes current tax
expense (income) and deferred income tax expense
(income). Tax is recorded in the income statement, unless
it refers to items that are recognized directly in equity, in
which case it is recognized in equity.
• Current tax
Current tax is the estimated amount of tax owed on taxa-
ble income for an accounting period. It is determined using
the tax rates applicable at the balance sheet date.
• Deferred income tax
Deferred income tax is measured using the asset-liability
approach of tax allocation for all timing differences bet-
ween the book value of the assets and liabilities and their
tax basis. Valuation of deferred tax assets and liabilities
depends on the way in which the group expects to recover
or settle the book value of the assets and liabilities using
the tax rates applicable at the balance sheet date.
A deferred tax asset is recognized only if it is probable that
the group will have future taxable profit against which the
asset may be utilized. Deferred tax assets are reduced to
the extent that it is no longer probable that sufficient taxa-
ble profit will be available.
The effect of possible changes in tax rates on previously
recorded deferred taxes is recognized in equity.