Ubisoft 2006 Annual Report Download - page 109
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 109 of the 2006 Ubisoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
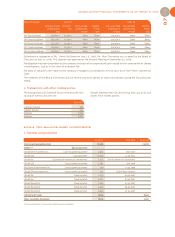
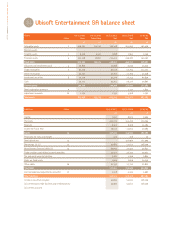
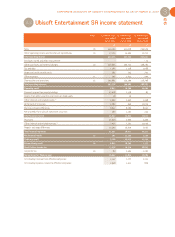
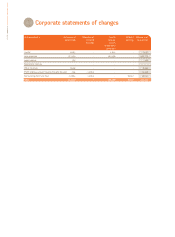
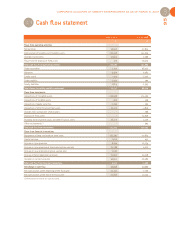
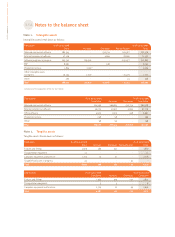
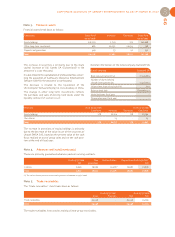
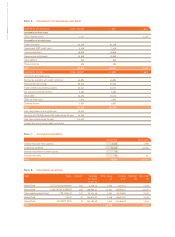
CORPORATE ACCOUNTS OF UBISOFT ENTERTAINMENT SA AS OF MARCH 31, 2007
97
3
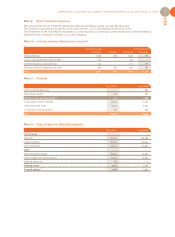
Commercial software:
Development costs of commercial software, whether pro-
duced in-house or outsourced, are recognized in the
“Intangible assets in progress” item (account 232) as deve-
lopment progresses. Once marketing begins, these costs
are transferred to the "Released software" or “External
developments” accounts (accounts 208).
Development costs of outsourced commercial software are
recognized under account 232 or advances and install-
ments, in accordance with the rules defined by France’s
Conseil d’Etat (CE 62547 of February 12, 1988, and CE
65009 of November 25, 1989) when they do not come
under the definition of an asset.
Development costs subcontracted to group subsidiaries
are recorded as subcontracting expenses and transferred
to fixed assets via a self-constructed assets account.
Commercial software and external developments are
amortized starting on the date of the product’s commer-
cial release.
When actual sales are less than projections and expected
return on sales, a provision for impairment is recorded.
Return on sales is determined on the basis of operating
result restated to reflect operating depreciation.
Brands:
Any brands acquired are recognized at their acquisition
cost.
Brands are not amortized. Impairment tests are performed
on brands at the close of each fiscal year, or more often if
there are indications of impairment. The recoverable value
of brands is then estimated on the basis of the change in
sales for the business division in question, its contribution
to the consolidated group’s income and its updated cash
flow. When this value is less than the book value, amorti-
zation is recorded.
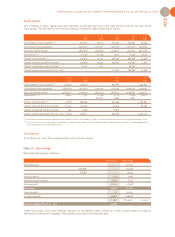
Tangible assets
These are shown at historical cost. The depreciation rates
applied are as follows:
- equipment: 5 years (straight-line),
- fixtures and fittings: 5 and 10 years (straight-line),
- computer equipment: 3 years (straight-line),
- office furniture: 10 years (straight-line).
Financial assets
Securities are valued at historical cost, excluding acquisi-
tion expenses.
The inventory value of the security is reviewed at the end of
each fiscal year based on the net position of the subsidiary in
question on that date, the stock market valuation on the
closing date if the company is listed on the stock exchange,
and/or on its medium-term profitability prospects.
A provision for depreciation is set up if necessary.
Directly held stocks are valued at their purchase price or
at market value if this is lower.
Deposits and guarantees are recognized on the basis of the
amounts paid.
Advances and installments paid
Advances and installments primarily involve distribution
and reproduction rights (licenses) acquired from other
publishers. The signing of licensing contracts entails the
payment of guaranteed amounts, These amounts are
recorded in account 409 at their net value (under Conseil
d’Etat rules 62547 of February 12, 1988, and 65009 of
November 25, 1989).
These advances and installments are reported on the
income statement based on the contracts signed with
publishers (either by the unit or based on gross margin or
sales) or, in the case of flat fees, amortized using the
straight-line method.
At the end of the fiscal year, the net book value is
compared with sales projections in light of the terms and
conditions of the contract. If projected sales are
insufficient, amortization will be recorded on the income
statement accordingly.
Trade receivables
Trade receivables are valued at their face value. Where
applicable, a provision for depreciation is recorded based
on the likelihood of their collection at the balance sheet
date.
Investment securities
Investment securities consist of interests in investment
funds and short-term investments, which are valued at
their purchase price or at their market value when this is
lower.
Conversion of debts and accounts receivable
expressed in foreign currencies
These were converted at the rates in effect at March 31,
2007. Any resulting translation gains or losses are shown
on the balance sheet under a specific heading. A provision
for foreign exchange risk is recorded if conversion reveals
the existence of unrealized losses.
Foreign exchange hedges
Since hedges are not allocated to specific transactions,
Ubisoft Entertainment SA has chosen not to use hedge
accounting to hedge its foreign exchange risk.
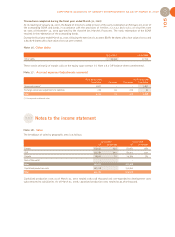
Provisions for risks and charges
Provisions for risks and charges are recorded when risks
and charges that have a clearly defined object, but which
are not certain to arise, are made likely by events that have
occurred or are in progress.
At March 31, 2007, provisions for risks and charges per-
tained only to foreign exchange risk related to discounting
of receivables and debts expressed in foreign currencies.