Foot Locker 2005 Annual Report Download - page 49
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 49 of the 2005 Foot Locker annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.receivables and payables approximates fair value due to the short-term nature of these assets and liabilities. Quoted
market prices of the same or similar instruments are used to determine fair value of long-term debt and forward foreign
exchange contracts. Discounted cash flows are used to determine the fair value of long-term investments and notes
receivable if quoted market prices on these instruments are unavailable.
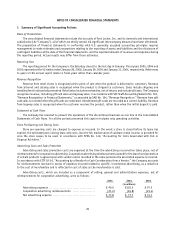
Income Taxes
The Company determines its deferred tax provision under the liability method, whereby deferred tax assets and
liabilities are recognized for the expected tax consequences of temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and
liabilities and their reported amounts using presently enacted tax rates. Deferred tax assets are recognized for tax credits
and net operating loss carryforwards, reduced by a valuation allowance, which is established when it is more likely than
not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities
of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
A taxing authority may challenge positions that the Company adopted in its income tax filings. Accordingly, the
Company may apply different tax treatments for transactions in filing its income tax returns than for income tax financial
reporting. The Company regularly assesses its tax position for such transactions and records reserves for those differences
when considered necessary.
Provision for U.S. income taxes on undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries is made only on those amounts in
excess of the funds considered to be permanently reinvested.
Pension and Postretirement Obligations
The discount rate selected to measure the present value of the Company’s benefit obligations as of January 28, 2006
was derived using a cash flow matching method whereby the Company compares the plans’ projected payment obligations
by year with the corresponding yield on the Citibank Pension Discount Curve. The cash flows are then discounted to their
present value and an overall discount rate is determined.
Insurance Liabilities
The Company is primarily self-insured for health care, workers’ compensation and general liability costs. Accordingly,
provisions are made for the Company’s actuarially determined estimates of discounted future claim costs for such risks
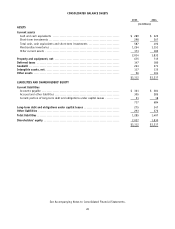
for the aggregate of claims reported and claims incurred but not yet reported. Self-insured liabilities totaled $16 million
at January 28, 2006 and $14 million at January 29, 2005. The Company discounts its workers’ compensation and
general liability using a risk-free interest rate. Imputed interest expense related to these liabilities was $1 million in each
of 2005, 2004 and 2003.
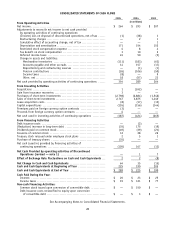
Accounting for Leases
The Company recognizes rent expense for operating leases as of the earlier of possession date for store leases or the
commencement of the agreement for a non-store lease. Rental expense, inclusive of rent holidays, concessions and tenant
allowances are recognized over the lease term on a straight-line basis. Contingent payments based upon sales and future
increases determined by inflation related indices cannot be estimated at the inception of the lease and accordingly, are
charged to operations as incurred.
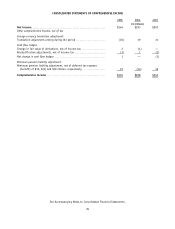
Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currency of the Company’s international operations is the applicable local currency. The translation
of the applicable foreign currency into U.S. dollars is performed for balance sheet accounts using current exchange rates
in effect at the balance sheet date and for revenue and expense accounts using the weighted-average rates of exchange
prevailing during the year. The unearned gains and losses resulting from such translation are included as a separate
component of accumulated other comprehensive loss within shareholders’ equity.
Reclassifications
Certain balances in prior years have been reclassified to conform to the presentation adopted in the current year.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements Not Previously Discussed Herein
In November 2004, the FASB issued SFAS No. 151, “Inventory Costs — an amendment of ARB 43, Chapter 4.” This
Statement amends the guidance to clarify that abnormal amounts of idle facility expense, freight, handling costs, and
wasted materials (spoilage) should be recognized as current-period charges. In addition, this Statement requires that
33