Volvo 2000 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2000 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
74
THE VOLVO GROUP
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Credit risks in financial instruments
Credit risk in financial investments
The liquidity in the Group is invested mainly in local cash
pools or directly with Volvo Treasury. This concentrates
the credit risk within the Group’s in-house bank. Volvo
Treasury invests the liquid funds in the money and capital
markets.
All investments must meet criteria for low credit risk
and high liquidity. In accordance with Volvo’s credit policy,
counterparties for both investments and transactions in
derivatives must have received a rating of “A” or better
from one of the well-established credit-rating institutions.
Counterparty risks
The derivative instruments used by Volvo to reduce its
foreign-exchange and interest-rate risk in turn give rise
to a counterparty risk, the risk that a counterparty will not
fulfill its part of a forward or option contract, and that a
potential gain will not be realized. Transactions with
derivative instruments are mainly conducted via Volvo
Treasury which means that the counterparty risk is con-
centrated within the Group’s in-house bank. Where
appropriate, the Volvo Group arranges master netting
agreements with the counterparty to reduce exposure.
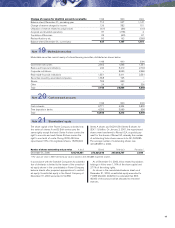
The credit exposure in interest-rate and foreign exchange
contracts is represented by the positive fair value – the
potential gain on these contracts – as of the reporting
date. The risk exposure is calculated daily. The credit risk
in futures contracts is limited through daily or monthly
cash settlements of the net change in value of open
contracts. The estimated exposure in foreign exchange
contracts, interest-rate swaps and futures and options
amounted to 2,559, 3,191 and 3 as of December 31,
2000.
Volvo does not have any significant exposure to an
individual customer or counterparty.
Calculation of fair value of financial instruments
Volvo has used generally accepted methods to calculate
the market value of the Group’s financial instruments as
of December 31, 1998 and 1999 and 2000. In the case
of instruments with maturities shorter than three months
– such as liquid funds and certain current liabilities as
well as certain short-term loans – the book value has
been assumed to closely approximate market value.
Official exchange rates and prices quoted in the open
market have been used initially for purposes of valuation.
In their absence, the valuation has been made by dis-
counting future cash flows at the market interest rate for
each maturity. These values are estimates and will not
necessarily be realized.
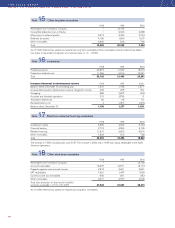
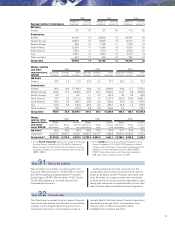
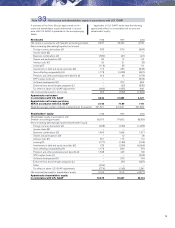
Estimated fair value of Volvo’s financial instruments
December 31, 1998 December 31, 1999 December 31, 2000
Book Fair Book Fair Book Fair
value value value value value value
Balance sheet items
Investments in shares and participations
fair value determinable11,110 851 3,537 2,212 27,589 20,955
fair value not determinable 2132 – 241 – 372 –
Long-term receivables and loans 31,349 31,362 36,240 36,751 28,646 29,095
Short-term receivables and loans 23,674 23,641 17,508 17,288 33,078 35,338
Marketable securities 7,168 7,562 20,956 21,534 9,568 9,603
Long-term loans and debts 26,012 26,882 32,514 32,394 40,670 41,792
Short-term loans 38,876 39,025 21,123 20,429 25,828 27,000
Off-balance-sheet items
Volvo Group outstanding currency risk related contracts (346) 3(881) (112) (1,570) (63) (3,154)
Volvo Group outstanding interest-risk related contracts (661) 3(281) 113 (368) 167 (24)
Volvo Group outstanding raw material contracts – (77) – – – 0
1 Pertains mainly to Volvo’s holdings in Mitsubishi Motors
Corporation 1999 as well as 2000, and in Scania AB 2000.
2 No single investment represents any significant amount.
3 Book values are included among items in the balance sheet.