Volvo 2000 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2000 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
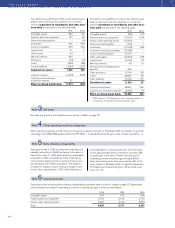
55
the time of acquisition (historical rates). Other income
statement items are translated at average rates. Translation
differences are credited to, or charged against, income in
the year in which they arise.
In the individual Group companies as well as in the
consolidated accounts, receivables and liabilities in for-
eign currency are valued at year-end exchange rates. In
appropriate cases, hedged receivables and liabilities are
valued at the underlying forward rate.
Gains and losses pertaining to hedges are reported at
the same time as gains and losses of the items hedged.
Received premiums or payments for currency options,
which hedge currency flows in business transactions, are
reported as income/expense during the contract period.
Gains/losses on outstanding currency futures at year-
end, which were entered into to hedge future commer-
cial currency flows, are reported at the same time as the
commercial flow is realized. For other currency futures
that do not fullfil the criteria for hedge accounting a full
market valuation is made on a portfolio basis and are
credited to, or charged against income.
In valuing financial assets and liabilities whose original
currency denomination has been changed as a result of
currency swap contracts, the loan amount is accounted
for translated to Swedish kronor taking into account the
swap contracts.
Exchange differences on loans and other financial
instruments in foreign currency, which are used to hedge
net assets in foreign subsidiaries and associated com-
panies, are offset against translation differences in the
shareholders’ equity of the respective companies.
Exchange gains and losses on payments during the
year and on the valuation of assets and liabilities in foreign
currencies at year-end are credited to, or charged against,
income before taxes and minority interests in the year
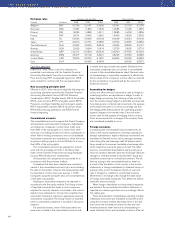
they arise. The more important exchange rates employed
are shown above.
Other financial instruments
Interest-rate contracts and foreign exchange contracts are
used to change the underlying financial asset and debt
structure and are reported as hedges against such assets
and debts.
Interest-rate contracts used as part of the management
of the Group’s short-term investments are valued together
with these investments in accordance with the portfolio
method. Provisions are made for unrealized losses in
excess of the unrealized gains within the portfolio.
Interest-rate contracts that do not fullfil the criteria of
hedge accounting are valued at the balance sheet date at
which time provisions for unrealized losses are made.
Capital expenditures
Capital expenditures include investments in buildings,
machinery and equipment, as well as in intangible assets.
Investments pertaining to assets under operating leases
are not included.
Investments in fixed assets included in the Group’s
cash flow statement include only capital expenditures that
have reduced the Group’s liquid funds during the year.
Depreciation and amortization of tangible
and intangible non-current assets
Depreciation is based on the historical cost of the
assets, adjusted in appropriate cases by write-downs,
and estimated economic lives. Capitalized type-specific
tools are generally depreciated over 2 to 8 years. The
depreciation period for assets under operating leases is
normally 3 to 5 years. Machinery is generally depreciated
over 5 to 20 years, and buildings over 25 to 50 years,
while the greater part of land improvements are depreci-
ated over 20 years. In connection with its participation in
aircraft engine projects with other companies, Volvo Aero
in certain cases pays an entrance fee. These entrance
fees are capitalized and depreciated over 5 to 10 years.
The difference between depreciation noted above and
depreciation allowable for tax purposes is reported by the
parent company and in the individual Group companies
as accumulated accelerated depreciation, which is in-
cluded in untaxed reserves. Consolidated reporting of
these items is described below under the heading
Deferred taxes, allocations and untaxed reserves.
Goodwill is included in intangible assets and amor-
tized on a straight-line basis over 5 to 20 years. The
goodwill pertaining to Volvo Construction Equipment,
Champion Road Machinery, The AGES Group, Prévost,
Nova BUS, Mexicana de Autobuses, Volvo Construction
Equipment Korea and Volvo Aero Norge are being amor-
tized over 20 years due to the holdings’ long-term and
strategic importance.
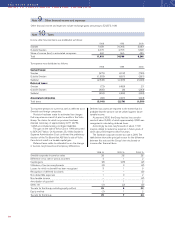
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost, in accordance
with the first-in, first-out method (FIFO), or net realizable
value. Provisions are made for obsolescence.
Marketable securities
Marketable securities are stated at the lower of cost or
market value in accordance with the portfolio method.
Liquid funds
Liquid funds include Cash and bank balances and mar-
ketable securities. Marketable securities to some extent
consist of interest bearing securities with maturities
exceeding three months. However, these securities have
high liquidity and can easily be converted to cash.
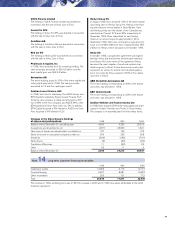
Postemployment benefits
Most of the Volvo Group’s pension commitments are met
through continuous payments to independent authorities
or bodies that administer the plans. Pension expense
corresponding to the fees paid for these defined-contri-
bution pension plans is reported continuously. In certain
of Volvo’s subsidiaries, mainly in Sweden and the U.S.,
there are defined benefit plans covering pensions and
healthcare benefits. For these plans, a provision and
annual pension expense are calculated based on the
current value of the earned future benefits. Provisions for
pensions and annual expenses related to defined pen-
sion and healthcare benefits are reported in Volvo’s con-
solidated balance sheet and income statement by apply-
ing the local rules and directives in each country.
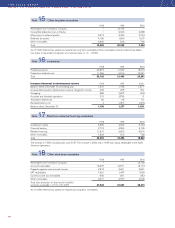
Net sales
The Group’s reported net sales pertain mainly to revenues
from sales of goods and services. Net sales are reduced
by the value of discounts granted and by returns.
Income from the sale of goods is recognized when the
goods are delivered to the customers. If however the sale
of goods is combined with a buy-back agreement or a
residual value guarantee, the sale is accounted for as an
operating lease transaction if significant risks are retained
in Volvo. Income from the sale of workshop services is rec-
ognized when the service is provided. Rental revenues and
interest income in conjunction with financial leasing or
installment contracts is recognized over the contract period.