PG&E 2011 Annual Report Download - page 93
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 93 of the 2011 PG&E annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.NOTE 11: FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS (Continued)
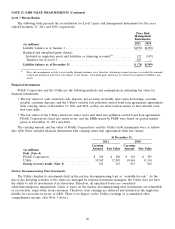
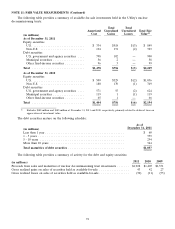
Trust Assets
The assets held by the nuclear decommissioning trusts, the rabbi trusts related to the non-qualified deferred
compensation plans, and the long-term disability trust are composed primarily of equity securities, debt securities,
and life insurance policies. In general, investments held in the trusts are exposed to various risks, such as interest
rate, credit, and market volatility risks.
Equity securities primarily include investments in common stock, which are valued based on unadjusted prices in
active markets for identical securities and are classified as Level 1. Equity securities also include commingled funds
composed of equity securities traded publicly on exchanges across multiple industry sectors in the U.S. and other
regions of the world, which are classified as Level 2. Price quotes for the assets held by these funds are readily
observable and available.
Debt securities are composed primarily of fixed-income securities that include U.S. government and agency
securities, municipal securities, and corporate debt securities. U.S. government and agency securities consist primarily
of treasury securities that are classified as Level 1 because the fair value is determined by observable market prices
in active markets. A market-based valuation approach is generally used to estimate the fair value of debt securities
classified as Level 2. Under a market approach, fair values are determined based on evaluated pricing data, such as
broker quotes, for similar securities adjusted for observable differences. Significant inputs used in the valuation
model generally include benchmark yield curves and issuer spreads. The external credit rating, coupon rate, and
maturity of each security are considered in the valuation, as applicable.
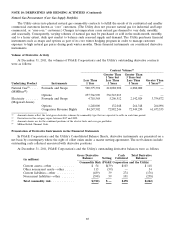
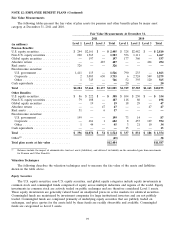
Price Risk Management Instruments
Price risk management instruments include physical and financial derivative contracts, such as forwards, swaps,
options, and CRRs that are either exchange-traded or over-the-counter traded. (See Note 10 above.)
Exchange-traded forwards and swaps that are valued using observable market prices for the underlying
commodity are classified as Level 1. Forwards and swaps transacted in the over-the-counter market that are identical
to exchange-traded forwards and swaps or are valued using market-corroborated inputs are classified as Level 2.
Forwards and swaps that are valued using unobservable data are classified as Level 3. These contracts are valued
using either estimated basis adjustments from liquid trading points or techniques, including extrapolation from
observable prices, when a contract term extends beyond a period for which market data is available.
Exchange-traded options are valued using observable market data and market-corroborated data and are
classified as Level 2. Over-the-counter options are valued using a standard option pricing model which includes
forward prices for the underlying commodity, time value at a risk-free rate, and volatility and are classified as
Level 3. For periods where market data is not available, the Utility extrapolates observable data using internal
models.
The Utility holds CRRs to hedge financial risk of CAISO-imposed congestion charges in the day-ahead market.
CRRs are valued based on prices observed in the auction which are extrapolated and discounted at the risk free rate.
Limited market data is available between auction dates; therefore, CRRs are classified as Level 3.
Transfers between Levels
PG&E Corporation and the Utility recognize any transfers between levels in the fair value hierarchy as of the
end of the reporting period. At December 31, 2011, the valuation of price risk management over-the-counter
forwards and swaps and exchange-traded options incorporated market observable and market corroborated inputs,
where certain previously-considered unobservable inputs became observable. Therefore, the Utility transferred these
instruments out of Level 3 and into Level 2. No significant transfers between Levels 1 and 2 occurred in the years
ended December 31, 2011 and 2010.
89