MasterCard 2011 Annual Report Download - page 140
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 140 of the 2011 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
The Company does not designate foreign currency derivatives as hedging instruments pursuant to the
accounting standards for derivative instruments and hedging activities. The Company records the change in the
estimated fair value of the outstanding derivatives at the end of the reporting period to its consolidated balance
sheet and consolidated statement of operations.
As of December 31, 2011, all contracts to purchase and sell foreign currency had been entered into with
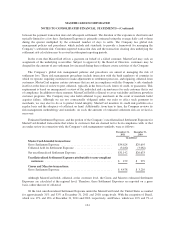
customers of MasterCard. MasterCard’s derivative contracts are summarized below:
December 31, 2011 December 31, 2010
Notional
Estimated
Fair Value 1Notional
Estimated
Fair Value 1
(in millions)
Commitments to purchase foreign currency ........ $ 21 $— $ 38 $1
Commitments to sell foreign currency ............ 279 2 148 (2)
Balance Sheet Location:
Accounts Receivable ...................... $ 4 $1
Other Current Liabilities .................. (2) (2)
1Amounts represent gross fair value amounts while these amounts may be netted for actual balance sheet
presentation.
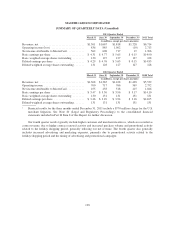
Amount and Location of Gain (Loss) Recognized in Income
Year Ended December 31,
2011 2010 2009
(in millions)
Foreign Currency Derivative Contracts1
General and administrative ..................................... $(6) $(17) $(12)
Revenues ................................................... (3) (3) (6)
Total ...................................................... $(9) $(20) $(18)
1Derivatives are not designated as hedging instruments pursuant to the accounting standards for derivative
instruments and hedging activities.
The currencies underlying the foreign currency forward contracts consist primarily of the Australian dollar,
British pound, Canadian dollar, Chinese renminbi, Euro, Hong Kong dollar, Korean won, Mexican peso, New
Zealand dollar, Thai baht and Turkish lira. The fair value of the foreign currency forward contracts generally
reflects the estimated amounts that the Company would receive (or pay), on a pre-tax basis, to terminate the
contracts at the reporting date based on broker quotes for the same or similar instruments. The terms of the
foreign currency forward contracts are generally less than 18 months. The Company had no deferred gains or
losses related to foreign exchange in accumulated other comprehensive income as of December 31, 2011 and
2010 as there were no derivative contracts accounted for under hedge accounting.
The Company’s derivative financial instruments are subject to both credit and market risk. Credit risk is the
risk of loss due to failure of the counterparty to perform its obligations in accordance with contractual terms.
Market risk is the risk of loss due to the potential change in an instrument’s value caused by fluctuations in
interest rates and other variables related to currency exchange rates. Credit and market risk related to derivative
instruments were not material at December 31, 2011 and 2010.
136