Harley Davidson 2012 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2012 Harley Davidson annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
83
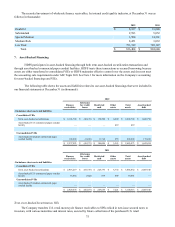
2010
AOCL
beginning
balance
Gross other
comprehensive
income (loss) Tax benefit
(expense)
Net other
comprehensive
income (loss)
Cumulative
effect of
accounting
change (a)
AOCL
ending
balance
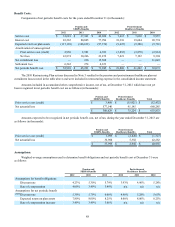
Foreign currency translation adjustment $ 46,102 $ 10,577 $ (1,128) $ 9,449 $ — $ 55,551
Unrealized gains (losses) on marketable
securities — (211) 78 (133) — (133)
Derivative financial instruments (8,940) (4,756) 1,784 (2,972) — (11,912)
Pension and postretirement benefit plans (451,577) 66,469 (24,620) 41,849 — (409,728)
Investment in retained securitization
interests (3,483) — — — 3,483 —
Accumulated other comprehensive loss $(417,898) $ 72,079 $ (23,886) $ 48,193 $ 3,483 $ (366,222)
(a) Net of tax of $1,959
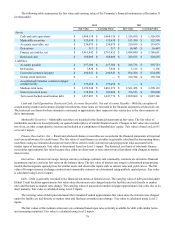
12. Debt
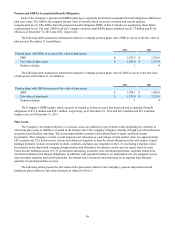
Debt with contractual terms less than one year is generally classified as short-term debt and consisted of the following as
of December 31 (in thousands):
2012 2011
Unsecured commercial paper $ 294,943 $ 838,486
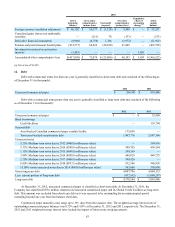
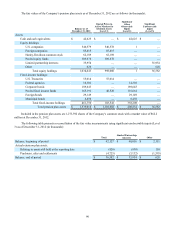
Debt with a contractual term greater than one year is generally classified as long-term debt and consisted of the following
as of December 31 (in thousands):
2012 2011
Unsecured commercial paper $ — $ 35,800
Bank borrowings
Credit facilities — 159,794
Secured debt
Asset-backed Canadian commercial paper conduit facility 175,658 —
Term asset-backed securitization debt 1,447,776 2,087,346
Unsecured notes
5.25% Medium-term notes due in 2012 ($400.0 million par value) — 399,916
5.75% Medium-term notes due in 2014 ($500.0 million par value) 499,705 499,544
1.15% Medium-term notes due in 2015 ($600.0 million par value) 599,269 —
3.88% Medium-term notes due in 2016 ($450.0 million par value) 449,829 449,775
2.70% Medium-term notes due in 2017 ($400.0 million par value) 399,929 —
6.80% Medium-term notes due in 2018 ($933.5 million par value) 932,540 948,958
15.00% senior unsecured notes due in 2014 ($600.0 million par value) 303,000 303,000
Gross long-term debt 4,807,706 4,884,133
Less: current portion of long-term debt (437,162)(1,040,247)
Long-term debt $ 4,370,544 $ 3,843,886
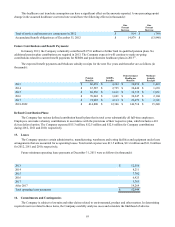
At December 31, 2012, unsecured commercial paper is classified as short-term debt. At December 31, 2011, the
Company has classified $195.6 million related to its unsecured commercial paper and its Global Credit Facilities as long-term
debt. This amount was excluded from short term debt as it was expected to be outstanding for an uninterrupted period
extending beyond one year from the balance sheet date.
Commercial paper maturities may range up to 365 days from the issuance date. The weighted-average interest rate of
outstanding commercial paper balances was 0.75% and 1.05% at December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The December 31,
2012 and 2011 weighted-average interest rates include the impact of interest rate swap agreements.