Harley Davidson 2012 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2012 Harley Davidson annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.80
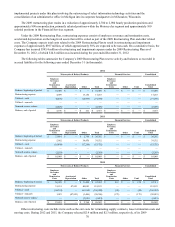
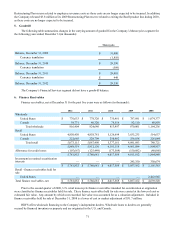
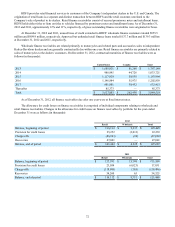
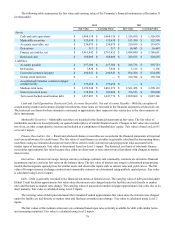
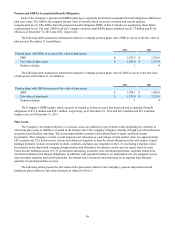
The fair value of the senior unsecured notes is estimated based upon rates currently available for debt with similar terms
and remaining maturities. Fair value is calculated using level 2 inputs.
The fair value of the debt related to term asset-backed securitization transactions is estimated based on pricing currently
available for transactions with similar terms and maturities. Fair value is calculated using level 2 inputs.
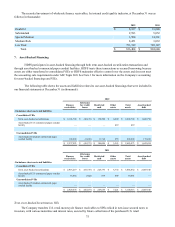
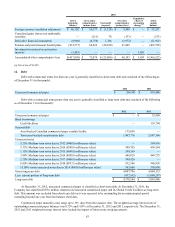
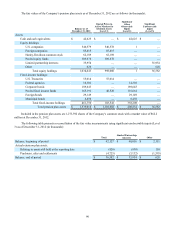
10. Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
The Company is exposed to certain risks such as foreign currency exchange rate risk, interest rate risk and commodity
price risk. To reduce its exposure to such risks, the Company selectively uses derivative financial instruments. All derivative
transactions are authorized and executed pursuant to regularly reviewed policies and procedures, which prohibit the use of
financial instruments for speculative trading purposes.
All derivative instruments are recognized on the balance sheet at fair value (see Note 9). In accordance with ASC Topic
815, "Derivatives and Hedging," the accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative instrument depends on whether it
has been designated and qualifies as part of a hedging relationship and, further, on the type of hedging relationship. Changes in
the fair value of derivatives that are designated as fair value hedges, along with the gain or loss on the hedged item, are
recorded in current period earnings. For derivative instruments that are designated as cash flow hedges, the effective portion of
gains and losses that result from changes in the fair value of derivative instruments is initially recorded in other comprehensive
income (OCI) and subsequently reclassified into earnings when the hedged item affects income. The Company assesses, at both
the inception of each hedge and on an on-going basis, whether the derivatives that are used in its hedging transactions are
highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the hedged items. Any ineffective portion is immediately recognized in
earnings. No component of a hedging derivative instrument’s gain or loss is excluded from the assessment of hedge
effectiveness. Derivative instruments that do not qualify for hedge accounting are recorded at fair value and any changes in fair
value are recorded in current period earnings.
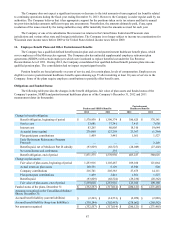
The Company sells its products internationally and in most markets those sales are made in the foreign country’s local
currency. As a result, the Company’s earnings can be affected by fluctuations in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to foreign
currency. The Company’s most significant foreign currency risk relates to the Euro, the Australian dollar, Japanese yen and the
Brazilian real. The Company utilizes foreign currency contracts to mitigate the effect of certain currencies’ fluctuations on
earnings. The foreign currency contracts are entered into with banks and allow the Company to exchange a specified amount of
foreign currency for U.S. dollars at a future date, based on a fixed exchange rate.
The Company utilizes commodity contracts to hedge portions of the cost of certain commodities consumed in the
Company’s motorcycle production and distribution operations.
The Company’s foreign currency contracts and commodity contracts generally have maturities of less than one year.
The Company’s earnings are affected by changes in interest rates. HDFS utilizes interest rate swaps to reduce the impact
of fluctuations in interest rates on its unsecured commercial paper by converting a portion from a floating rate basis to a fixed
rate basis. The fair value of HDFS' interest rate swaps is determined using pricing models that incorporate quoted prices for
similar assets and observable inputs such as interest rates and yield curves.