Berkshire Hathaway 2004 Annual Report Download - page 34
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 34 of the 2004 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.33
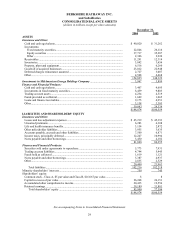
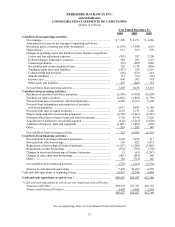
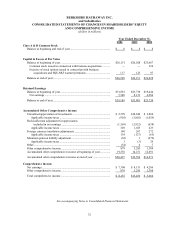
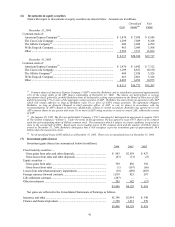
BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC.
and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2004
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices
(a) Nature of operations and basis of consolidation
Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (“Berkshire” or “Company”) is a holding company owning subsidiaries engaged
in a number of diverse business activities. The most important of these are property and casualty
insurance businesses conducted on both a primary and reinsurance basis. Further information regarding
these businesses and Berkshire’ s other reportable business segments is contained in Note 21. Berkshire
consummated a number of business acquisitions over the past three years which are discussed in Note 2.
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Berkshire consolidated with
the accounts of all of its subsidiaries and affiliates in which Berkshire holds a controlling financial
interest as of the financial statement date. Normally control reflects ownership of a majority of the
voting interests. Other factors considered in determining whether control is held include whether
Berkshire provides significant financial support as a result of its authority to purchase or sell assets or
make other operating decisions that significantly affect the entity’ s results of operations and whether
Berkshire bears a majority of the financial risks.
Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated. Certain amounts in 2003 and 2002 have
been reclassified to conform with the current year presentation.
(b) Use of estimates in preparation of financial statements
The preparation of the Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting
principles (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amount of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amount of
revenues and expenses during the period. In particular, estimates of unpaid losses and loss adjustment
expenses and related recoverables under reinsurance for property and casualty insurance are subject to
considerable estimation error due to the inherent uncertainty in projecting ultimate claim amounts that
will be reported and settled over a period of many years. In addition, estimates and assumptions
associated with the amortization of deferred charges reinsurance assumed, the determination of fair
value of certain invested assets and related impairments, and the determination of goodwill impairments
require considerable judgment by management. Actual results may differ from the estimates and
assumptions used in preparing the Consolidated Financial Statements.
(c) Cash equivalents
Cash equivalents consist of funds invested in U.S. Treasury Bills, money market accounts, and in other
investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased.
(d) Investments
Berkshire’ s management determines the appropriate classifications of investments in fixed maturity
securities and equity securities at the time of acquisition and re-evaluates the classifications at each
balance sheet date. Berkshire’ s investments in fixed maturity and equity securities are primarily
classified as available-for-sale, except for certain securities held by finance businesses which are
classified as held-to-maturity.
Held-to-maturity investments are carried at amortized cost, reflecting Berkshire’ s intent and ability to hold
the securities to maturity. Available-for-sale securities are stated at fair value with net unrealized gains
or losses reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
Investment gains and losses arise when investments are sold (as determined on a specific identification
basis) or are other-than-temporarily impaired and are included in the Consolidated Statements of
Earnings. If in management’ s judgment, a decline in the value of an investment below cost is other-
than-temporary, the cost of the investment is written down to fair value with a corresponding charge to
earnings. Factors considered in determining whether an impairment exists include: the financial
condition, business prospects and creditworthiness of the issuer, the length of time that the asset’ s fair
value has been less than cost, and Berkshire’ s ability and intent to hold such investment until the fair
value recovers.