Berkshire Hathaway 2003 Annual Report Download - page 34
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 34 of the 2003 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.33
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(l) Losses and loss adjustment expenses (Continued)
lower rate for post-2002 claims reflects the lower interest rate environment prevailing in the United
States. The discount rates are the same rates used under statutory accounting principles. The periodic
discount accretion is included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings as a component of losses and
loss adjustment expenses.
(m) Deferred charges reinsurance assumed
The excess of estimated liabilities for claims and claim costs over the consideration received with respect to
retroactive property and casualty reinsurance contracts that provide for indemnification of insurance risk
is established as a deferred charge at inception of such contracts. The deferred charges are subsequently
amortized using the interest method over the expected claim settlement periods. The periodic
amortization charges are reflected in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings as losses
and loss adjustment expenses.
Changes to the expected timing and estimated amount of loss payments produce changes in the unamortized
deferred charge balance. Such changes in estimates are accounted for retrospectively with the net effect
included in amortization expense in the period of the change.
(n) Reinsurance
Provisions for losses and loss adjustment expenses are reported in the accompanying Consolidated
Statements of Earnings after deducting amounts recovered and estimates of amounts recoverable under
reinsurance contracts. Reinsurance contracts do not relieve the ceding company of its obligations to
indemnify policyholders with respect to the underlying insurance and reinsurance contracts.
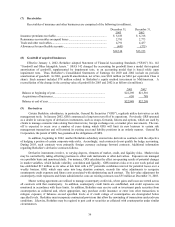
(o) Insurance premium acquisition costs
Certain costs of acquiring insurance premiums are deferred, subject to ultimate recoverability, and charged
to income as the premiums are earned. Acquisition costs consist of commissions, premium taxes,
advertising and other underwriting costs. The recoverability of premium acquisition costs, generally,
reflects anticipation of investment income. The unamortized balances of deferred premium acquisition
costs are included in other assets and were $1,278 million and $1,303 million at December 31, 2003 and
2002, respectively.
(p) Foreign currency
The accounts of foreign-based subsidiaries are measured using the local currency as the functional currency.
Revenues and expenses of these businesses are translated into U.S. dollars at the average exchange rate
for the period. Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate as of the end of the reporting
period. Gains or losses from translating the financial statements of foreign-based operations are
included in shareholders’ equity as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income. Gains
and losses arising from other transactions denominated in a foreign currency are included in the
Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
(q) Deferred income taxes
Deferred income taxes are calculated under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are
recorded based on differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities at
the enacted tax rates. Changes in deferred income tax assets and liabilities that are associated with
components of other comprehensive income, primarily unrealized investment gains, are charged or
credited directly to other comprehensive income. Otherwise, changes in deferred income tax assets and
liabilities are included as a component of income tax expense.
(r) Accounting pronouncements to be adopted in 2004
In December 2003, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued a revision to Statement No.
132, “Employers’ Disclosures about Pension Plans and Other Post Retirement Benefits”, which requires
additional quantitative and qualitative disclosures concerning plan assets and benefit obligations. Certain
of the new disclosures are effective immediately for U.S. plans and are included in Note 17.