Safeway 2010 Annual Report Download - page 60
Download and view the complete annual report
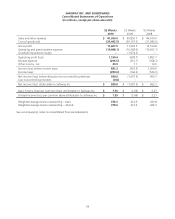
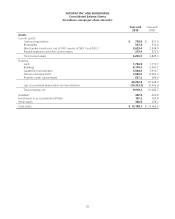
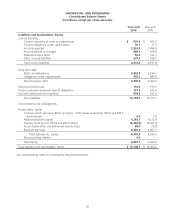
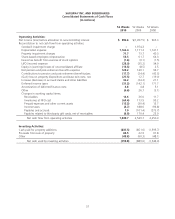
Please find page 60 of the 2010 Safeway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SAFEWAY INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
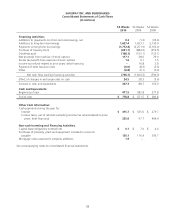
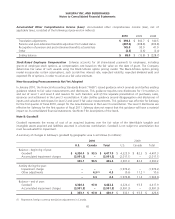
Financial Instruments
Interest rate swaps. The Company has, from time to time, entered into interest rate swap agreements to change its
portfolio mix of fixed- and floating-rate debt to more desirable levels. Interest rate swap agreements involve the exchange
with a counterparty of fixed- and floating-rate interest payments periodically over the life of the agreements without
exchange of the underlying notional principal amounts. The differential to be paid or received is recognized over the life
of the agreements as an adjustment to interest expense. The Company’s counterparties have been major financial
institutions.
Energy contracts. The Company has entered into contracts to purchase electricity and natural gas at fixed prices for a
portion of its energy needs. Safeway expects to take delivery of the electricity and natural gas in the normal course of
business. Contracts that qualify for the normal purchase exception under derivatives and hedging accounting guidance
are not marked to market. Energy purchased under these contracts is expensed as delivered.
Warrants. Blackhawk issued warrants to third parties to purchase shares of Blackhawk common stock. The warrants are
accounted for as liability awards and marked-to-market every period. The liability is calculated using the Black-Sholes
model and included in Accrued Claims and Other Liabilities on the balance sheet. Since there is no active market for these
warrants, the valuation model uses unobservable pricing inputs and management estimates.
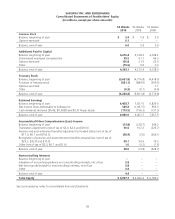
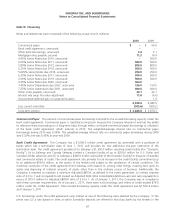
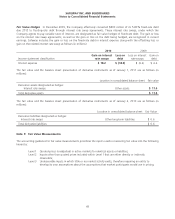
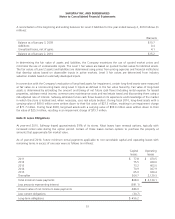
Fair Value of Financial Instruments Disclosures of the fair value of certain financial instruments are required, whether
or not recognized in the balance sheet. The Company estimated the fair values presented below using appropriate
valuation methodologies and market information available as of year end. Considerable judgment is required to develop
estimates of fair value, and the estimates presented are not necessarily indicative of the amounts that the Company could
realize in a current market exchange. The use of different market assumptions or estimation methodologies could have a
material effect on the estimated fair values. Additionally, the fair values were estimated at year end, and current estimates
of fair value may differ significantly from the amounts presented.
The following methods and assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of each class of financial instruments:
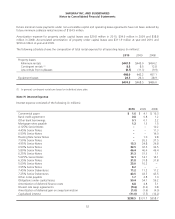
Cash and equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable. The carrying amount of these items approximates fair
value.
Long-term debt, including current maturities. Market values quoted in public markets are used to estimate the fair value
of publicly traded debt. To estimate the fair value of debt issues that are not quoted in public markets, the Company uses
those interest rates that are currently available to it for issuance of debt with similar terms and remaining maturities as a
discount rate for the remaining principal payments.
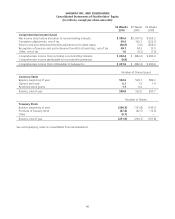
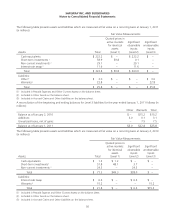
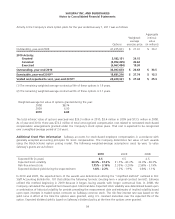
Store Lease Exit Costs and Impairment Charges Safeway regularly reviews its stores’ operating performance and
assesses the Company’s plans for certain store and plant closures. Losses related to the impairment of long-lived assets
are recognized when expected future cash flows are less than the asset’s carrying value. The Company evaluates the
carrying value of the assets in relation to its expected future cash flows. If the carrying value is greater than the future
cash flows, a provision is made for the impairment of the assets to write the assets down to estimated fair value. Fair
value is determined by estimating net future cash flows, discounted using a risk-adjusted rate of return. The Company
calculates impairment on a store-by-store basis. These provisions are recorded as a component of operating and
administrative expense.
When stores that are under long-term leases close, the Company records a liability for the future minimum lease
payments and related ancillary costs, net of estimated cost recoveries that may be achieved through subletting properties
or through favorable lease terminations, discounted using a risk-adjusted rate of interest. This liability is recorded at the
time the store is closed. Activity included in the reserve for store lease exit costs is disclosed in Note C.
44