The Hartford 2013 Annual Report Download - page 191
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 191 of the 2013 The Hartford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F-55
International program
The Company formerly offered certain variable annuity products in Japan with GMWB or GMAB riders, which are bifurcated
embedded derivatives (“International program product derivatives”). The GMWB provides the policyholder with a guaranteed remaining
balance (“GRB”) which is generally equal to premiums less withdrawals. If the policyholder’s account value is reduced to the specified
level through a combination of market declines and withdrawals but the GRB still has value, the Company is obligated to continue to
make annuity payments to the policyholder until the GRB is exhausted. Certain contract provisions can increase the GRB at
contractholder election or after the passage of time. The GMAB provides the policyholder with their initial deposit in a lump sum after a
specified waiting period. The notional amount of the International program product derivatives are the foreign currency denominated
GRBs converted to U.S. dollars at the current foreign spot exchange rate as of the reporting period date.
The Company enters into derivative contracts (“International program hedging instruments”) to hedge a portion of the capital market
risk exposures associated with the guaranteed benefits associated with the international variable annuity contracts. During 2013, the
Company expanded its hedging program to substantially reduce equity and foreign currency exchange risk. The program is primarily
focused on the risks that have been reinsured to the Company’s U.S. legal entities although certain hedges, predominantly options, are
also held directly in HLIKK . The hedging derivatives collectively held in these entities are comprised of equity futures, options, swaps
and currency forwards and options to hedge against a decline in the debt and equity markets or changes in foreign currency exchange
rates and the resulting statutory surplus and capital impact primarily arising from GMDB, GMIB and GMWB obligations issued in
Japan. The Company also enters into foreign currency denominated interest rate swaps and swaptions to hedge the interest rate exposure
related to the potential annuitization of certain benefit obligations.
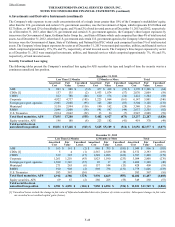
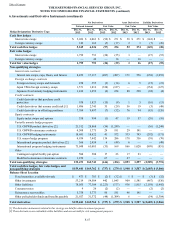
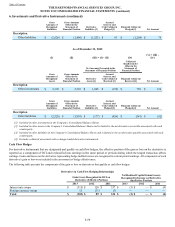
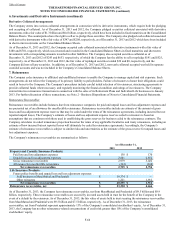
The following table represents notional and fair value for the international program hedging instruments.
Notional Amount Fair Value
December 31,
2013 December 31,
2012 December 31,
2013 December 31,
2012
Credit derivatives $ 350 $ 350 $ 5 $ 28
Currency forwards [1] 13,410 9,327 (60) (87)
Currency options 12,066 10,342 (54) (24)
Equity futures 999 2,332 — —
Equity options 3,051 3,952 (30) 47
Equity swaps 4,269 2,617 (119) (12)
Customized swaps — 899 — (11)
Interest rate futures 952 634 — —
Interest rate swaps and swaptions 37,951 32,632 225 228
Total $ 73,048 $ 63,085 $ (33) $ 169
[1] As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, net notional amounts are $(1.8) billion and $0.1 billion, respectively, which include $5.8 billion and $4.7
billion, respectively, related to long positions and $7.6 billion and $4.6 billion, respectively, related to short positions.
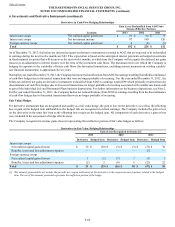
Contingent capital facility put option
The Company entered into a put option agreement that provides the Company the right to require a third-party trust to purchase, at any
time, The Hartford’s junior subordinated notes in a maximum aggregate principal amount of $500. Under the put option agreement, The
Hartford will pay premiums on a periodic basis and will reimburse the trust for certain fees and ordinary expenses.
Modified coinsurance reinsurance contracts
As of December 31, 2013 the Company had approximately $1.3 billion of invested assets supporting other policyholder funds and benefits
payable reinsured under a modified coinsurance arrangement in connection with the sale of the Individual Life business structured as a
reinsurance transaction. The assets are held in a trust established by the Company. The Company pays or receives cash quarterly to settle
the results of the reinsured business, including the investment results. As a result of this modified coinsurance arrangement, the Company
has an embedded derivative that transfers to the reinsurer certain unrealized changes in fair value due to interest rate and credit risks of
these assets. The notional amounts of the reinsurance contracts are the invested assets supporting the reinsured reserves and are carried at
fair value.
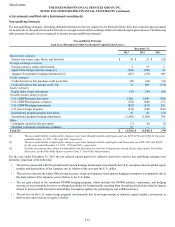
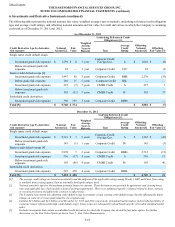
Table of Contents THE HARTFORD FINANCIAL SERVICES GROUP, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (continued)
6. Investments and Derivative Instruments (continued)