The Hartford 2013 Annual Report Download - page 102
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 102 of the 2013 The Hartford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
102
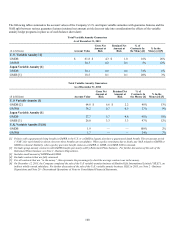
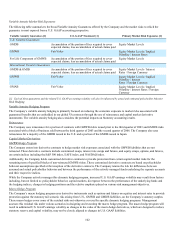
Variable Annuity Market Risk Exposures
The following table summarizes the broad Variable Annuity Guarantees offered by the Company and the market risks to which the
guarantee is most exposed from a U.S. GAAP accounting perspective.
Variable Annuity Guarantees [1] U.S. GAAP Treatment [1] Primary Market Risk Exposures [1]
U.S. Variable Guarantees
GMDB Accumulation of the portion of fees required to cover
expected claims, less accumulation of actual claims paid Equity Market Levels
GMWB Fair Value Equity Market Levels / Implied
Volatility / Interest Rates
For Life Component of GMWB Accumulation of the portion of fees required to cover
expected claims, less accumulation of actual claims paid Equity Market Levels
International Variable Guarantees
GMDB & GMIB Accumulation of the portion of fees required to cover
expected claims, less accumulation of actual claims paid Equity Market Levels / Interest
Rates / Foreign Currency
GMWB Fair Value Equity Market Levels / Implied
Volatility / Interest
Rates / Foreign Currency
GMAB Fair Value Equity Market Levels / Implied
Volatility / Interest Rates / Foreign
Currency
[1] Each of these guarantees and the related U.S. GAAP accounting volatility will also be influenced by actual and estimated policyholder behavior.
Risk Hedging
Variable Annuity Hedging Program
The Company’s variable annuity hedging is primarily focused on reducing the economic exposure to market risks associated with
guaranteed benefits that are embedded in our global VA contracts through the use of reinsurance and capital market derivative
instruments. The variable annuity hedging also considers the potential impacts on Statutory accounting results.
Reinsurance
The Company uses reinsurance for a portion of contracts with GMWB riders issued prior to the third quarter of 2003 and GMWB risks
associated with a block of business sold between the third quarter of 2003 and the second quarter of 2006. The Company also uses
reinsurance for a majority of the GMDB issued in the U.S. and a portion of the GMDB issued in Japan.
Capital Market Derivatives
GMWB Hedge Program
The Company enters into derivative contracts to hedge market risk exposures associated with the GMWB liabilities that are not
reinsured. These derivative contracts include customized swaps, interest rate swaps and futures, and equity swaps, options, and futures,
on certain indices including the S&P 500 index, EAFE index, and NASDAQ index.
Additionally, the Company holds customized derivative contracts to provide protection from certain capital market risks for the
remaining term of specified blocks of non-reinsured GMWB riders. These customized derivative contracts are based on policyholder
behavior assumptions specified at the inception of the derivative contracts. The Company retains the risk for differences between
assumed and actual policyholder behavior and between the performance of the actively managed funds underlying the separate accounts
and their respective indices.
While the Company actively manages this dynamic hedging program, increased U.S. GAAP earnings volatility may result from factors
including, but not limited to: policyholder behavior, capital markets, divergence between the performance of the underlying funds and
the hedging indices, changes in hedging positions and the relative emphasis placed on various risk management objectives.
Macro Hedge Program
The Company’s macro hedging program uses derivative instruments such as options and futures on equities and interest rates to provide
protection against the statutory tail scenario risk arising from U.S., GMWB and GMDB liabilities, on the Company’s statutory surplus.
These macro hedges cover some of the residual risks not otherwise covered by specific dynamic hedging programs. Management
assesses this residual risk under various scenarios in designing and executing the macro hedge program. The macro hedge program will
result in additional U.S. GAAP earnings volatility as changes in the value of the macro hedge derivatives, which are designed to reduce
statutory reserve and capital volatility, may not be closely aligned to changes in U.S. GAAP liabilities.