Pitney Bowes 2012 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2012 Pitney Bowes annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
PITNEY BOWES INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Tabular dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
54
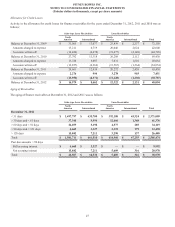
The effective tax rate for 2011 includes $90 million of tax benefits from the IRS tax settlements (see Other Matters below), a $34 million
tax benefit from the sale of non-U.S. leveraged lease assets and a $4 million charge from the write-off of deferred tax assets associated
with the expiration of out-of-the-money vested stock options and the vesting of restricted stock units previously granted to our employees.
In addition, the effective tax rate for 2011 was increased due to a reduced tax benefit associated with the goodwill impairment charges.
The effective tax rate for 2010 includes $16 million of tax benefits associated with previously unrecognized deferred taxes on outside
basis differences, a $15 million charge for the write-off of deferred tax assets associated with the expiration of out-of-the-money vested
stock options and the vesting of restricted stock units previously granted to our employees and a $9 million charge for the write-off of
deferred tax assets related to the U.S. health care reform legislation that eliminated the tax deduction for retiree health care costs to the
extent of federal subsidies received by companies that provide retiree prescription drug benefits equivalent to Medicare Part D coverage.
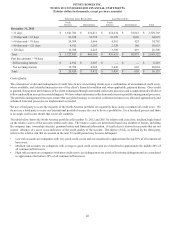
The items described in the immediately preceding paragraphs that generated significant tax rate fluctuations are not expected to recur in
future periods.
On January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (the Act) was signed into law. Among others provisions, the Act retroactively
extends through 2013 certain expired provisions including the research credit and controlled foreign corporation look-thru rules. As a
result, we expect an immaterial decrease to our 2013 tax rate.
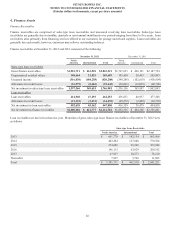
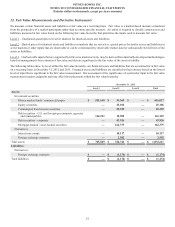
The items accounting for the difference between income taxes computed at the federal statutory rate and our provision for income taxes
consist of the following:
Years Ended December 31,
2012 2011 2010
Federal statutory provision $ 211,614 $ 170,289 $ 194,668
State and local income taxes 1,694 16,327 14,729
Impact of non-U.S. leveraged lease asset sales (30,367)(31,423)—
Other impact of foreign operations 22,699 16,388 13,556
Tax exempt income/reimbursement (1,992)(2,674) (2,352)
Federal income tax credits/incentives (8,918)(10,741) (7,580)
Unrealized stock compensation benefits 3,456 3,538 15,149
Resolution of U.S. tax examinations (47,380)(94,225) (8,230)
U.S. health care reform tax change —— 9,070
Outside basis differences —— (15,798)
Other, net (501)131 386
Provision for income taxes $ 150,305 $ 67,610 $ 213,598
Other impacts of foreign operations include income of foreign affiliates taxed at rates other than the 35% U.S. statutory rate, the accrual
or release of tax uncertainty amounts related to foreign operations, the tax impacts of foreign earnings repatriation and the U.S. foreign
tax credit impacts of other foreign income taxed in the U.S.