MetLife 2000 Annual Report Download - page 29
Download and view the complete annual report
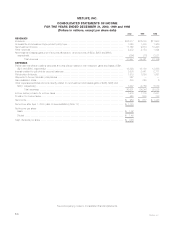
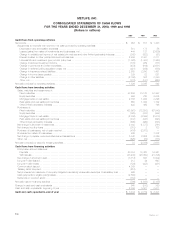
Please find page 29 of the 2000 MetLife annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
The Company must effectively manage, measure and monitor the market risk associated with its invested assets and interest rate sensitive
insurance contracts. It has developed an integrated process for managing risk, which it conducts through its Corporate Risk Management Department,
several asset/liability committees and additional specialists at the business segment level. The Company has established and implemented comprehen-
sive policies and procedures at both the corporate and business segment level to minimize the effects of potential market volatility.
Market Risk Exposures
The Company has exposure to market risk through its insurance operations and investment activities. For purposes of this disclosure, ‘‘market risk’’
is defined as the risk of loss resulting from changes in interest rates, equity prices and foreign exchange rates.
Interest rates. The Company’s exposure to interest rate changes results from its significant holdings of fixed maturities, as well as its interest rate
sensitive liabilities. The fixed maturities include U.S. and foreign government bonds, securities issued by government agencies, corporate bonds and
mortgage-backed securities, all of which are mainly exposed to changes in medium- and long-term treasury rates. The interest rate sensitive liabilities for
purposes of this disclosure include guaranteed interest contracts and fixed annuities, which have the same interest rate exposure (medium- and long-
term treasury rates) as the fixed maturities. The Company employs product design, pricing and asset/liability management strategies to reduce the
adverse effects of interest rate volatility. Product design and pricing strategies include the use of surrender charges or restrictions on withdrawals in some
products. Asset/liability management strategies include the use of derivatives, the purchase of securities structured to protect against prepayments,
prepayment restrictions and related fees on mortgage loans and consistent monitoring of the pricing of the Company’s products in order to better match
the duration of the assets and the liabilities they support.
Equity prices. The Company’s investments in equity securities expose it to changes in equity prices. It manages this risk on an integrated basis
with other risks through its asset/liability management strategies. The Company also manages equity price risk through industry and issuer diversification
and asset allocation techniques.
Foreign exchange rates. The Company’s exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates against the U.S. dollar results from its holdings in non-
U.S. dollar denominated fixed maturity securities and equity securities and through its investments in foreign subsidiaries. The principal currencies which
create foreign exchange rate risk in the Company’s investment portfolios are Canadian dollars, Euros, German marks, French francs, Spanish pesetas,
Mexican pesos and British pounds. The Company mitigates the majority of its fixed maturities’ foreign exchange rate risk through the utilization of foreign
currency swaps and forward contracts. Through its investments in foreign subsidiaries, the Company is primarily exposed to the Spanish peseta,
Mexican peso and South Korean won. The Company has denominated substantially all assets and liabilities of its foreign subsidiaries in their respective
local currencies, thereby minimizing its risk to foreign exchange rate fluctuations.
Risk Management
Corporate risk management. MetLife has established several financial and non-financial senior management committees as part of its risk
management process. These committees manage capital and risk positions, approve asset/liability management strategies and establish appropriate
corporate business standards.
MetLife also has a separate Corporate Risk Management Department, which is responsible for risk throughout MetLife and reports directly to
Metropolitan Life’s Chief Actuary. The Corporate Risk Management Department’s primary responsibilities consist of:
)implementing a board of directors-approved corporate risk framework, which outlines the Company’s approach for managing risk on an
enterprise-wide basis;
)developing policies and procedures for managing, measuring and monitoring those risks identified in the corporate risk framework;
)establishing appropriate corporate risk tolerance levels;
)deploying capital on a risk-adjusted basis; and
)reporting on a periodic basis to the Audit Committee of the Holding Company’s board of directors and various financial and non-financial senior
management committees.
Asset/liability management. At MetLife, asset/liability management is the responsibility of the General Account Portfolio Management Department
(‘‘GAPM’’), the operating business segments and various GAPM boards. The GAPM boards are comprised of senior officers from the investment
department, senior managers from each business segment and the Chief Actuary. The GAPM boards’ duties include setting broad asset/liability
management policy and strategy, reviewing and approving target portfolios, establishing investment guidelines and limits, and providing oversight of the
portfolio management process.
The portfolio managers and asset sector specialists, who have responsibility on a day-to-day basis for risk management of their respective investing
activities, implement the goals and objectives established by the GAPM boards. The goals of the investment process are to optimize after-tax, risk-
adjusted investment income and after-tax, risk-adjusted total return while ensuring that the assets and liabilities are managed on a cash flow and duration
basis. The risk management objectives established by the GAPM boards stress quality, diversification, asset/liability matching, liquidity and investment
return.
Each of MetLife’s business segments has an asset/liability officer who works with portfolio managers in the investment department to monitor
investment, product pricing, hedge strategy and liability management issues. MetLife establishes target asset portfolios for each major insurance product,
which represent the investment strategies used to profitably fund its liabilities within acceptable levels of risk. These strategies include objectives for
effective duration, yield curve sensitivity, convexity, liquidity, asset sector concentration and credit quality.
To manage interest rate risk, the Company performs periodic projections of asset and liability cash flows to evaluate the potential sensitivity of its
securities investments and liabilities to interest rate movements. These projections involve evaluating the potential gain or loss on most of the Company’s
in-force business under various increasing and decreasing interest rate environments. The Company has developed models of its in-force business that
reflect specific product characteristics and include assumptions based on current and anticipated experience regarding lapse, mortality and interest
crediting rates. In addition, these models include asset cash flow projections reflecting interest payments, sinking fund payments, principal payments,
bond calls, mortgage prepayments and defaults. New York Insurance Department regulations require that MetLife perform some of these analyses
annually as part of the annual proof of the sufficiency of its regulatory reserves to meet adverse interest rate scenarios.
Hedging activities. MetLife’s risk management strategies incorporate the use of various interest rate derivatives that are used to adjust the overall
duration and cash flow profile of its invested asset portfolios to better match the duration and cash flow profile of its liabilities to reduce interest rate risk.
Such instruments include interest rate swaps, futures and caps. MetLife also uses foreign currency swaps and forward contracts to hedge its foreign
currency denominated fixed income investments.
MetLife, Inc.
26