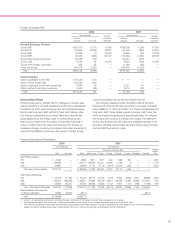
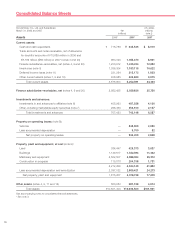
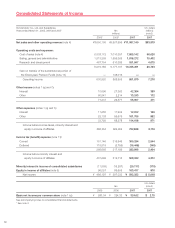
Honda 2007 Annual Report Download - page 78
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 78 of the 2007 Honda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
76
1. General and Summary of Significant
Accounting Policies
(a) Description of Business
Honda Motor Co., Ltd. (the “Company”) and its subsidiaries
(collectively “Honda”) develop, manufacture, distribute and
provide financing for the sale of its motorcycles, automobiles
and power products. Honda’s manufacturing operations are
principally conducted in 32 separate factories, four of which
are located in Japan. Principal overseas manufacturing facili-
ties are located in the United States of America, Canada,
Mexico, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, China,
India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, the Philippines, Taiwan,
Thailand, Vietnam, Brazil and Turkey.
(b) Basis of Presenting Consolidated Financial Statements
The Company and its domestic subsidiaries maintain their
books of account in conformity with financial accounting
standards of Japan, and its foreign subsidiaries generally
maintain their books of account in conformity with those of
the countries of their domicile.
The consolidated financial statements presented herein
have been prepared in a manner and reflect the adjustments
which are necessary to conform them with U.S. generally
accepted accounting principles.
(c) Consolidation Policy
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts
of the Company, its subsidiaries and those variable interest
entities where the Company is the primary beneficiary under
the Financial Accounting Standard Boards (FASB) Interpreta-
tion (FIN) No. 46 (revised December 2003), “Consolidation of
Variable Interest Entities”. All significant intercompany
balances and transactions have been eliminated in
consolidation.
Investments in affiliates in which the Company has the
ability to exercise significant influence over their operating
and financial policies, but where the Company does not have
a controlling financial interest are accounted for using the
equity method.
(d) Use of Estimates
Management of Honda has made a number of estimates and
assumptions relating to the reporting of assets, liabilities, rev-
enues and expenses, and the disclosure of contingent assets
and liabilities to prepare these consolidated financial state-
ments in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting
principles. Significant items subject to such estimates and
assumptions include, but are not limited to, allowance for
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Honda Motor Co., Ltd. and Subsidiaries
credit losses, losses on lease residual values, realizable
values of inventories, realization of deferred tax assets,
impairment of long-lived assets, product warranty obliga-
tions, and the fair values of assets and obligations related to
employee benefits. Actual results could differ from those
estimates.
(e) Revenue Recognition
Sales of manufactured products are recognized when per-
suasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has
occurred, title and risk of loss have passed to the customers,
the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is
probable.
Honda provides dealer incentives passed on to the end
customers generally in the form of below-market interest rate
loans or lease programs. The amount of interest or lease
subsidies paid is the difference between the amount offered
to retail customers and a market-based interest or lease rate.
Honda also provides dealer incentives retained by the dealer,
which generally represent discounts provided by Honda to
the dealers. These incentives are classified as a reduction of
sales revenue as the consideration is paid in cash and Honda
does not receive an identifiable benefit in exchange for this
consideration. The estimated costs are accrued at the time
the product is sold to the dealer.
Operating lease revenues are recorded on a straight-line
basis over the term of the lease.
Interest income from finance receivables is recognized
using the interest method. Finance receivable origination fees
and certain direct origination costs are deferred, and the net
fee or cost is amortized using the interest method over the
contractual life of the finance receivables.
Finance subsidiaries of the Company periodically sell
finance receivables. Gain or loss is recognized equal to the
difference between the cash proceeds received and the car-
rying value of the receivables sold and is recorded in the
period in which the sale occurs. Honda allocates the
recorded investment in finance receivables between the
portion(s) of the receivables sold and portion(s) retained
based on the relative fair values of those portions on the date
the receivables are sold. Honda recognizes gains or losses
attributable to the change in the fair value of the retained
interests, which are recorded at estimated fair value and
accounted for as “trading” securities. Honda determines the
fair value of the retained interests by discounting the future
cash flows. Those cash flows are estimated based on pre-
payments, credit losses and other information as available
and are discounted at a rate which Honda believes is com-
mensurate with the risk free rate plus a risk premium. A