Honda 2007 Annual Report Download - page 110
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 110 of the 2007 Honda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
108
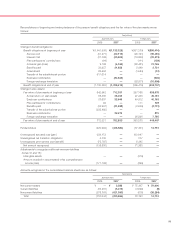
Held-to-maturity securities
The fair value of held-to-maturity security was estimated
using quoted market prices.
Convertible notes and convertible preferred stock
investment
Convertible instruments were bifurcated into two portions for
accounting purposes. The note and preferred stock portions
of these convertible instruments were treated as available-
for-sale and were marked-to-market through other compre-
hensive income (loss). The fair value was determined based
on an analysis of interest rate movements and an assess-
ment of credit worthiness. The embedded derivative was
marked-to-market through the statement of income and fair
value was estimated using a trinomial convertible bond
pricing model.
Honda is a party to derivative financial instruments in the
normal course of business to reduce their exposure to
fluctuations in foreign exchange rates and interest rates.
Currency swap agreements are used to convert long-term
debt denominated in a certain currency to long-term debt
denominated in other currencies. Foreign currency forward
exchange contracts and purchased option contracts are
normally used to hedge sale commitments denominated in
foreign currencies (principally U.S. dollars). Foreign currency
written option contracts are entered into in combination with
purchased option contracts to offset premium amounts to be
paid for purchased option contracts. Interest rate swap
agreements are mainly used to convert floating rate financ-
ing, such as commercial paper, to (normally three-five years)
fixed rate financing in order to match financing costs with
income from finance receivables. These instruments involve,
to varying degrees, elements of credit, exchange rate and
interest rate risks in excess of the amount recognized in the
consolidated balance sheets.
The aforementioned instruments contain an element of
risk in the event the counterparties are unable to meet the
terms of the agreements. However, Honda minimizes the risk
exposure by limiting the counterparties to major international
banks and financial institutions meeting established credit
guidelines. Management of Honda does not expect any
counterparty to default on its obligations and, therefore, does
not expect to incur any losses due to counterparty default.
Honda generally does not require or place collateral for these
financial instruments.
Foreign currency forward contracts and currency swap
agreements are agreements to exchange different currencies
at a specified rate on a specific future date. Foreign currency
option contracts are contracts that allow the holder of the
option the right but not the obligation to exchange different
currencies at a specified rate on a specific future date. For-
eign currency forward exchange contracts, foreign currency
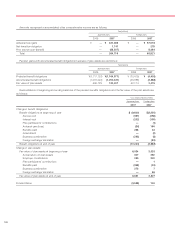
option contracts and currency swap agreements outstanding
at March 31, 2006 were ¥898,125 million, ¥176,548 million
and ¥584,358 million, respectively and totaled ¥1,659,031
million. At March 31, 2007, foreign currency forward
exchange contracts, foreign currency option contracts and
currency swap agreements outstanding were ¥978,994 mil-
lion ($8,293 million), ¥5,793 million ($49 million) and
¥608,534 million ($5,155 million), respectively and totaled
¥1,593,321 million ($13,497 million).
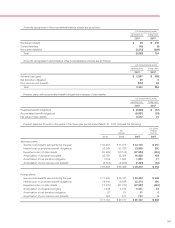
Cash flow hedge
The Company applies hedge accounting for certain foreign
currency forward exchange contracts related to forecasted
foreign currency transactions between the Company and its
subsidiaries. Changes in the fair value of derivative financial
instruments designated as cash flow hedges are recognized
in other comprehensive income (loss). The amounts are
reclassified into earnings in the same period when forecasted
hedged transactions affect earnings. The amount recognized
in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) was ¥64
million loss in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2006 and ¥20
million ($0 million) gain in the fiscal year ended March 31,
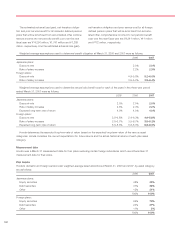
Debt
The fair values of bonds and notes were estimated based on
the quoted market prices for the same or similar issues. The
fair value of long-term loans was estimated by discounting
future cash flows using rates currently available for loans of
similar terms and remaining maturities. The carrying amounts
of short-term bank loans and commercial paper approximate
fair values because of the short maturity of these instruments.
Foreign exchange and interest rate instruments
The fair values of foreign currency forward exchange
contracts and foreign currency option contracts were esti-
mated by obtaining quotes from banks. The fair values of
currency swap agreements and interest rate swap agree-
ments were estimated by discounting future cash flows using
rates currently available for these instruments of similar terms
and remaining maturities.
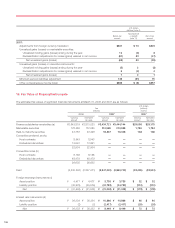
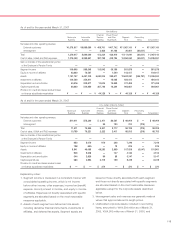
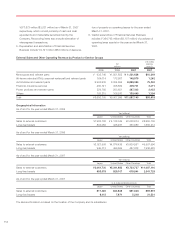
17. Risk Management Activities and Derivative Financial Instruments