HSBC 2005 Annual Report Download - page 164
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 164 of the 2005 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
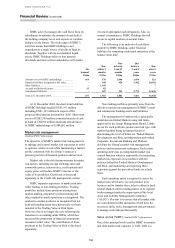 154
154 -
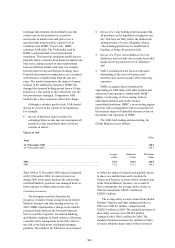 155
155 -
 156
156 -
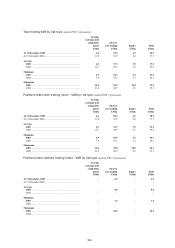 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366 -
 367
367 -
 368
368 -
 369
369 -
 370
370 -
 371
371 -
 372
372 -
 373
373 -
 374
374 -
 375
375 -
 376
376 -
 377
377 -
 378
378 -
 379
379 -
 380
380 -
 381
381 -
 382
382 -
 383
383 -
 384
384 -
 385
385 -
 386
386 -
 387
387 -
 388
388 -
 389
389 -
 390
390 -
 391
391 -
 392
392 -
 393
393 -
 394
394 -
 395
395 -
 396
396 -
 397
397 -
 398
398 -
 399
399 -
 400
400 -
 401
401 -
 402
402 -
 403
403 -
 404
404 -
 405
405 -
 406
406 -
 407
407 -
 408
408 -
 409
409 -
 410
410 -
 411
411 -
 412
412 -
 413
413 -
 414
414 -
 415
415 -
 416
416 -
 417
417 -
 418
418 -
 419
419 -
 420
420 -
 421
421 -
 422
422 -
 423
423 -
 424
424
 |
 |

HSBC HOLDINGS PLC
Financial Review (continued)
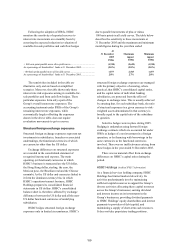
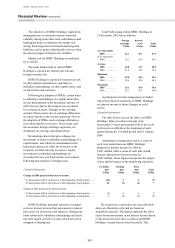
162
Reputational risk management
(Unaudited information)
The safeguarding of HSBC’s reputation is of
paramount importance to its continued prosperity
and is the responsibility of every member of staff.
Reputational risks can arise from social, ethical or
environmental issues, or as a consequence of
operational risk events. As a banking group, HSBC’s
good reputation depends upon the way in which it
conducts its business, but it can also be affected by
the way in which clients, to whom it provides
financial services, conduct themselves.
Reputational risks are considered and assessed
by the Board, the Group Management Board, the
Risk Management Meeting, subsidiary company
boards, board committees and/or senior management
during the formulation of policy and the
establishment of HSBC standards. Standards on all
major aspects of business are set for HSBC and for
individual subsidiaries, businesses and functions.
These policies, which are an integral part of the
internal control systems, are communicated through
manuals and statements of policy and are
promulgated through internal communications and
training. The policies set out operational procedures
in all areas of reputational risk, including money
laundering deterrence, environmental impact, anti-
corruption measures and employee relations.
Management in all operating entities is required
to establish a strong internal control structure to
minimise the risk of operational and financial failure,
and to ensure that a full appraisal of reputational
implications is made before strategic decisions are
taken. The Group Internal Audit function monitors
compliance with policies and standards.
Risk management of insurance
operations
(Forms part of the audited financial statements)
Insurance risk
Within its service proposition, HSBC offers its
personal and commercial customers a wide range of
insurance products, many of which complement
other bank and consumer finance products.
Both life and non-life insurance is underwritten.
Underwriting occurs in nine countries through 27
licensed insurers, principally in the UK, Hong Kong,
Mexico, Brazil, the US and Argentina.
Life insurance contracts include participating
business (with discretionary participation features)
such as endowments and pensions, credit life
business in respect of income and payment
protection, annuities, term assurance and critical
illness covers.
Non-life insurance contracts include motor, fire
and other damage, accident, repayment protection
and a limited amount of commercial and liability
business.
The principal insurance risk faced by HSBC is
that the costs of claims combined with acquisition
and administration costs may exceed the aggregate
amount of premiums received and investment
income. HSBC manages its insurance risks through
the application of formal underwriting, reinsurance
and claims procedures. These procedures are
designed also to ensure compliance with regulations.
The Group’s overall approach to insurance risk
is to maintain a good diversification of insurance
business by type and geography, and to focus on
risks that are straightforward to manage and
frequently are directly related to the underlying
banking activity (for example, with credit life
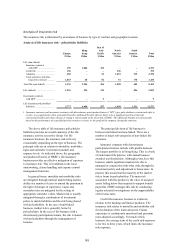
products). The following tables provide an analysis
of the insurance risk exposures by geography and by
type of business. These tables demonstrate the
Group’s diversification of risk and the strong
emphasis on personal lines. Personal lines tend to be
higher volume and with lower individual value than
commercial lines, which further diversifies the risk.
Separate tables are provided for life and non-life
business, reflecting their very distinct risk
characteristics. Life business tends to be longer term
than non-life and also frequently involves an element
of savings and investment in the premium. For this
reason, the life insurance risk table provides an
analysis of the insurance liabilities as the best
available overall measure of the insurance exposure.
By contrast for non-life business, the table uses
written premium as representing the best available
measure of risk exposure.
Both life and non-life business insurance risks
are controlled through a combination of local and
central procedures and policies. These include a
centralised approach to the authorisation to write
certain classes of business, with restrictions applying
particularly to commercial and liability non-life
business. For life business in particular, use is also
made of ALCOs in order to monitor the risk
exposures. Market risk limits are also applied
centrally as an additional control over the extent of
insurance risk that is retained.
As indicated in the specific comments relating
to particular classes, use is also made of reinsurance
as a means of further mitigating exposure, in
particular to aggregations as a result of catastrophe
risk.
