NetSpend 2014 Annual Report Download - page 49
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 49 of the 2014 NetSpend annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.headquartered in Shanghai, China. TSYS’ equity investments are recorded initially at cost and subsequently
adjusted for equity in earnings, cash contributions and distributions, and foreign currency translation adjustments.
GOODWILL: Goodwill results from the excess of cost over the fair value of net assets of businesses acquired.
Goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are tested for impairment at least annually. Intangible
assets with estimable useful lives are amortized over their respective estimated useful lives to their estimated
residual values.
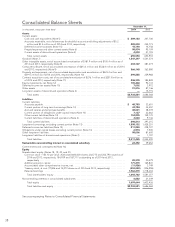
Equity investment goodwill, which is not reported as goodwill in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet, but
is reported as a component of the equity investment, was $51.4 million as of December 31, 2014.
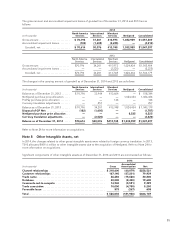
OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS: Identifiable intangible assets relate primarily to customer relationships,
databases, channel relationships, covenants-not-to-compete, trade names and trade associations resulting from
acquisitions. These identifiable intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line method over periods not
exceeding the estimated useful lives, which range from three to ten years. Intangible assets with estimable useful
lives are amortized over their respective estimated useful lives to their estimated residual values, and reviewed
for impairment in accordance with GAAP. Amortization expenses are charged to selling, general and
administrative expenses in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income.
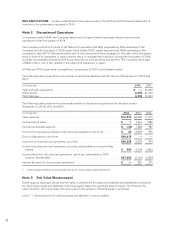
FAIR VALUES OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS: The Company uses financial instruments in the normal course
of its business. The carrying values of cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued salaries
and employee benefits, and other current liabilities approximate their fair value due to the short-term maturities
of these assets and liabilities. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt and obligations under capital
leases is not significantly different from its carrying value.
Investments in equity investments are accounted for using the equity method of accounting and pertain to
privately held companies for which fair value is not readily available. The Company believes the fair values of its
investments in equity investments exceed their respective carrying values.
IMPAIRMENT OF LONG-LIVED ASSETS: The Company reviews long-lived assets, such as property and
equipment and intangibles subject to amortization, including contract acquisition costs and certain computer
software, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an
asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the
carrying amount of an asset to estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset.
If upon a triggering event the Company determines that the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated
undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount
of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. Assets to be disposed of would be separately presented in the
balance sheet and reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell, and would no
longer be depreciated. The assets and liabilities of a disposed group classified as held for sale would be
presented separately in the appropriate asset and liability sections of the balance sheet.
TRANSACTION PROCESSING PROVISIONS: The Company has recorded an accrual for contract
contingencies (performance penalties) and processing errors. A significant number of the Company’s contracts
with large clients contain service level agreements which can result in TSYS incurring performance penalties if
contractually required service levels are not met. When providing for these accruals, the Company takes into
consideration such factors as the prior history of performance penalties and processing errors incurred, actual
contractual penalties inherent in the Company’s contracts, progress towards milestones and known processing
errors not covered by insurance.
These accruals are included in other current liabilities in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Increases and decreases in transaction processing provisions are charged to cost of services in the Company’s
Consolidated Statements of Income, and payments or credits for performance penalties and processing errors
are charged against the accrual.
CARDHOLDERS’ RESERVE: The Company is exposed to losses due to cardholder fraud, payment defaults and
other forms of cardholder activity as well as losses due to non-performance of third parties who receive
cardholder funds for transmittal to the Issuing Banks (banks that issue MasterCard International or Visa USA,Inc.
46