Lexmark 2011 Annual Report Download - page 94
Download and view the complete annual report
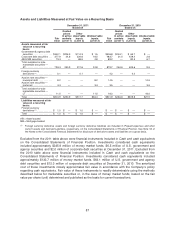
Please find page 94 of the 2011 Lexmark annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Additionally, as indicated in the table above, the Company transferred, on a gross basis, $11.1 million
of corporate debt and asset-backed securities from Level 2 to Level 3 during 2010. The Company has
been unable to corroborate the consensus price of these securities with a sufficient level of observable
market data to maintain Level 2 classification. The Company also transferred, on a gross basis, $8.4
million of corporate debt and mortgage-backed securities from Level 3 to Level 2 as the Company was
able to obtain information demonstrating that the prices were observable in the market as of
December 31, 2010.
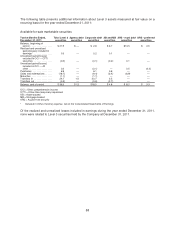
Valuation Techniques
Marketable securities — general
The Company evaluates its marketable securities in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards
Board (“FASB”) guidance on accounting for investments in debt and equity securities, and has
determined that all of its investments in marketable securities should be classified as available-for-sale
and reported at fair value. The Company generally employs a market approach in valuing its
marketable securities, using quoted market prices or other observable market data when available. In
certain instances, when observable market data is lacking, fair values are determined using valuation
techniques consistent with the income approach whereby future cash flows are converted to a single
discounted amount.
The Company uses multiple third parties to report the fair values of the securities in which Lexmark is
invested, though the responsibility of valuation remains with the Company’s management. Most of the
securities’ fair values are based upon a consensus price method, whereby prices from a variety of
industry data providers are input into a distribution-curve based algorithm to determine the most
appropriate fair value. The Company utilizes various sources of pricing as well as trading and other
market data in its process of corroborating fair values and testing default level assumptions. The
Company assesses the quantity of pricing sources available, variability in the prices provided, trading
activity, and other relevant data in performing this process.
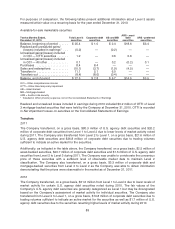
Government and agency debt securities
The Company’s government and agency debt securities are generally highly liquid investments having
multiple sources of pricing with low variability among the data providers. The consensus price method,
described previously, is used to select the most appropriate price. Fair value measurements for U.S.
government securities are most often based on quoted market prices in active markets and are
generally categorized as Level 1. U.S. agency debt securities and international government debt
securities may exhibit lower levels of market activity and are classified into the most appropriate level
according to the process described in the paragraph above.
Corporate debt securities
The corporate debt securities in which the Company is invested most often have multiple sources of
pricing with relatively low dispersion and are valued using the consensus price method. The fair values
of these securities are generally classified as Level 2. Certain of these securities, however, are
classified as Level 3 because the Company was unable to corroborate the consensus price of these
securities with a sufficient level of observable market data due to a low number of observed trades or
pricing sources. In addition, certain corporate debt securities are classified as Level 1 due to trading
volumes sufficient to indicate an active market for the securities.
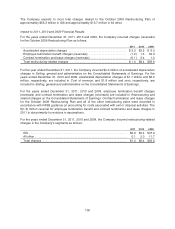
Smaller amounts of commercial paper and certificates of deposit, which generally have shorter
maturities and less frequent trades, are also grouped into this fixed income sector. Such securities are
valued via mathematical calculations using observable inputs until such time that market activity
reflects an updated price. The fair values of these securities are typically classified as Level 2
measurements.
90