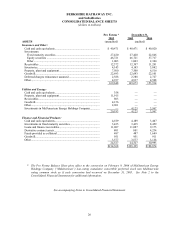
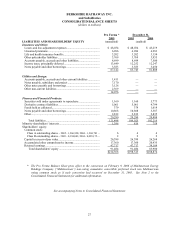
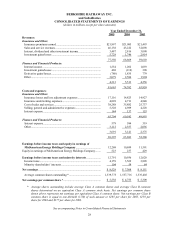
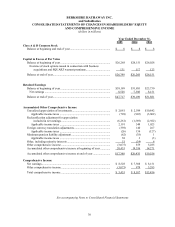
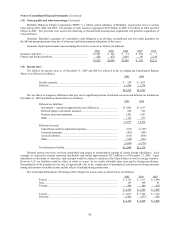
Berkshire Hathaway 2005 Annual Report Download - page 34
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 34 of the 2005 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.33
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(i) Property, plant and equipment (Continued)
Property, plant and equipment is evaluated for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the
carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. Upon the occurrence of a triggering event, the asset is reviewed
to assess whether the estimated undiscounted cash flows expected from the use of the asset plus residual value from
the ultimate disposal exceeds the carrying value of the asset. If the carrying value exceeds the estimated recoverable
amounts, the asset is written down to the estimated discounted present value of the expected future cash flows from
using the asset. The resulting impairment loss is reflected in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
(j) Goodwill
Goodwill represents the difference between purchase cost and the fair value of net assets acquired in business
acquisitions. Goodwill is tested for impairment using a variety of methods at least annually and impairments, if any,
are charged to earnings. Key assumptions used in the testing include, but are not limited to, the use of an
appropriate discount rate and estimated future cash flows. In estimating cash flows, the Company incorporates
current market information as well as historical factors. During 2005 and 2004, the Company did not record any
goodwill impairments.
(k) Revenue recognition
Insurance premiums for prospective property/casualty insurance and reinsurance and health reinsurance policies are
earned in proportion to the level of insurance protection provided. In most cases, premiums are recognized as
revenues ratably over the term of the contract with unearned premiums computed on a monthly or daily pro rata
basis. Premiums for retroactive reinsurance property/casualty policies are earned at the inception of the contracts.
Premiums for life reinsurance contracts are earned when due.
Premiums earned are stated net of amounts ceded to reinsurers. Premiums are estimated with respect to certain
reinsurance contracts written during the period where reports from ceding companies for the period are not
contractually due until after the balance sheet date. For policies containing experience rating provisions, premiums
are based upon estimated loss experience under the contract.
Sales revenues derive from the sales of manufactured products and goods acquired for resale. Revenues from sales are
recognized upon passage of title to the customer, which generally coincides with customer pickup, product delivery
or acceptance, depending on terms of the sales arrangement.
Service revenues derive primarily from pilot training and flight operations and flight management activities. Service
revenues are recognized as the services are performed. Services provided pursuant to a contract are either
recognized over the contract period, or upon completion of the elements specified in the contract, depending on the
terms of the contract.
Interest income from investments in bonds and loans is earned under the constant yield method and includes accrual of
interest due under terms of the investment security or loan agreement as well as amortization of acquisition
premiums and accruable discounts. In determining the constant yield for mortgage-backed securities, anticipated
counterparty prepayments are estimated and evaluated periodically. Dividends from equity securities are accrued
and earned on the ex-dividend date.
(l) Losses and loss adjustment expenses
Liabilities for unpaid losses and loss adjustment expenses represent estimated claim and claim settlement costs of
property/casualty insurance and reinsurance contracts with respect to losses that have occurred as of the balance
sheet date. The liabilities for losses and loss adjustment expenses are recorded at the estimated ultimate payment
amounts, except that amounts arising from certain workers’ compensation reinsurance business are discounted as
discussed below. Estimated ultimate payment amounts are based upon (1) individual case estimates, (2) reports of
losses from policyholders and (3) estimates of incurred but not reported (“IBNR”) losses.
The estimated liabilities of workers’ compensation claims assumed under certain reinsurance contracts are carried in the
Consolidated Balance Sheets at discounted amounts. Discounted amounts are based upon an annual discount rate of
4.5% for claims arising prior to 2003 and 1% for claims arising after 2002, consistent with discount rates used under
statutory accounting principles. The periodic discount accretion is included in the Consolidated Statements of
Earnings as a component of losses and loss adjustment expenses.
(m) Deferred charges reinsurance assumed
The excess of estimated liabilities for claims and claim costs over the consideration received with respect to retroactive
property and casualty reinsurance contracts that provide for indemnification of insurance risk is established as a
deferred charge at inception of such contracts. The deferred charges are subsequently amortized using the interest
method over the expected claim settlement periods. The periodic amortization charges are reflected in the
accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings as losses and loss adjustment expenses.
Changes to the expected timing and estimated amount of loss payments produce changes in the unamortized deferred
charge balance. Such changes in estimates are accounted for retrospectively with the net effect included in
amortization expense in the period of the change.