Avon 2003 Annual Report Download - page 44
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 44 of the 2003 Avon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
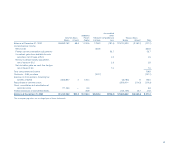
who are Avon’s customers. Avon’s internal financial systems accumulate
revenues as orders are shipped to the Representative. Since Avon reports
revenue upon delivery, revenues recorded in the financial system must be
reduced for an estimate of the financial impact of those orders shipped but
not delivered at the end of each reporting period. Avon uses estimates in
determining revenue and operating profit for orders that have been shipped
but not delivered as of the end of the period. These estimates are based on
daily sales levels, delivery lead times, gross margin and variable expenses.
Avon also estimates an allowance for sales returns based on historical expe-
rience with product returns. In addition, Avon estimates an allowance for
doubtful accounts receivable based on an analysis of historical data and
current circumstances.
Other Revenue — Other revenue includes shipping and handling fees charged
to Representatives.
Cash and Cash Equivalents — Cash equivalents are stated at cost plus
accrued interest, which approximates fair value. Cash equivalents are high-
quality, short-term money market instruments with an original maturity of
three months or less and consist of time deposits with a number of U.S.
and non-U.S. commercial banks and money market fund investments.
Inventories — Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost
is determined using the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) method for all inventories.
Avon classifies inventory into various categories based upon their stage in
the product life cycle, future marketing sales plans and disposition process.
Avon assigns a degree of obsolescence risk to products based on this classifi-
cation to determine the level of obsolescence provision.
Property, Plant and Equipment — Property, plant and equipment are stated
at cost. Substantially all buildings, improvements and equipment are depreci-
ated using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives. Estimated
useful lives for buildings and improvements range from approximately 15 to
45 years and equipment range from three to 15 years. Upon disposal of prop-
erty, plant and equipment, the cost of the assets and the related accumulated
depreciation are removed from the accounts and the resulting gain or loss is
reflected in earnings. Costs associated with repairs and maintenance
activities are expensed as incurred.
Avon capitalizes interest on borrowings during the active construction period
of major capital projects. Capitalized interest is added to the cost of the under-
lying asset and depreciated over the useful lives of the assets. For 2003, 2002
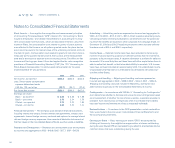
and 2001, Avon capitalized $1.6, $1.0 and $0.0 of interest, respectively.
Deferred Software — In accordance with Statement of Position 98-1,
“Accounting for the Costs of Computer Software Developed or Obtained for
Internal Use,” certain systems development costs related to the purchase, devel-
opment and installation of computer software are capitalized and amortized over
the estimated useful life of the related project, not to exceed five years. Costs
incurred prior to the development stage, as well as maintenance, training costs,
and general and administrative expenses are expensed as incurred. Unamortized
deferred software costs totaled $73.7 and $86.3 at December 31, 2003 and
2002, respectively, and were included in Other assets on the Consolidated
Balance Sheets.
Investments in Debt and Equity Securities — Debt and equity securities that
have a readily determinable fair value and that management does not intend
to hold to maturity are classified as available-for-sale and carried at fair value.
Unrealized holding gains and losses are recorded as a separate component
of Shareholders’ equity (deficit), net of deferred taxes.
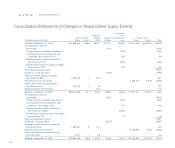
Avon recognizes revenue upon delivery of products to its
independent Representatives, less discounts, commissions,
taxes, estimated product returns and other deductions.
63