Avon 2003 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2003 Avon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Avon’s diversified global portfolio of businesses has demonstrated
that the effects of weak economies and currency fluctuations in
certain countries may be offset by strong results in others.
Avon’s long-term borrowings and interest rate swaps were analyzed at year-end
to determine their sensitivity to interest rate changes. Based on the outstanding
balance of all these financial instruments at December 31, 2003, a hypothetical
50 basis point change (either an increase or a decrease) in interest rates prevail-
ing at that date, sustained for one year, would not represent a material potential
change in fair value, earnings or cash flows. This potential change was calcu-
lated based on discounted cash flow analyses using interest rates comparable
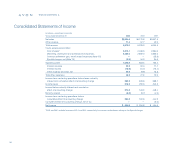
to Avon’s current cost of debt. In 2003, interest expense decreased $18.7 pri-
marily due to a decline in domestic interest rates.
Foreign Currency Risk
Avon is exposed to changes in financial market conditions in the normal
course of its operations, primarily due to international businesses and trans-
actions denominated in foreign currencies and the use of various financial
instruments to fund ongoing activities.
Avon uses foreign currency forward contracts and options to hedge portions
of its forecasted foreign currency cash flows resulting from intercompany roy-
alties, intercompany loans, and other third-party and intercompany foreign
currency transactions where there is a high probability that anticipated expo-
sures will materialize. These contracts have been designated as cash flow
hedges. At December 31, 2003, the primary currencies for which Avon has net
underlying foreign currency exchange rate exposure are the U.S. dollar versus
the Argentine peso, Brazilian real, British pound, Chinese renminbi, the Euro,
Japanese yen, Mexican peso, Philippine peso, Polish zloty, Russian ruble and
Venezuelan bolivar.
Avon also enters into foreign currency forward contracts and options to pro-
tect against the adverse effects that exchange rate fluctuations may have on
the earnings of its foreign subsidiaries. These derivatives do not qualify for
hedge accounting and, therefore, the gains and losses on these derivatives
have been recognized in earnings each reporting period.
Avon uses foreign currency forward contracts and foreign currency denominated
debt to hedge the foreign currency exposure related to the net assets of certain
of its foreign subsidiaries. At December 31, 2003, Avon had a Japanese yen
denominated note payable to hedge Avon’s net investment in its Japanese
subsidiary (see Note 4, Debt and Other Financing).
Avon’s hedges of its foreign currency exposure are not designed to and there-
fore cannot entirely eliminate the effect of changes in foreign exchange rates
on Avon’s consolidated financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
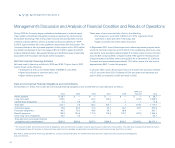
At December 31, 2003, Avon held foreign currency forward and option con-
tracts to buy and sell foreign currencies, including cross-currency contracts
to sell one foreign currency for another, with notional amounts in U.S. dollars
as follows:
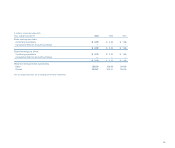
Buy Sell
Australian dollar $ 1.8 $ —
Brazilian real — 4.0
British pound 7.1 69.7
Canadian dollar — 54.0
Czech koruna 7.3 9.8
Euro 128.8 9.8
Hungarian forint — 35.4
Japanese yen 42.7 10.8
Mexican peso — 35.0
Polish zloty 49.9 17.6
Russian ruble — 30.9
Other currencies 2.6 3.4
Total $240.2 $280.4
Certain of Avon subsidiaries hold U.S. dollar denominated assets, primarily to
minimize foreign-currency risk and provide liquidity. At December 31, 2003,
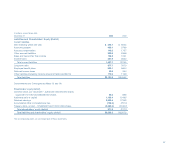
Avon’s subsidiary in Argentina held U.S. dollar denominated assets totaling
$6.0. At December 31, 2002, Avon subsidiaries that held U.S. dollar denomi-
nated assets included Mexico ($23.5), Argentina ($12.4), Venezuela ($6.8) and
Brazil ($7.6). For the years ended December 31, 2003 and 2002, Other expense
(income), net included net transaction losses of $2.8 and net transaction gains
of $27.8, respectively, related to these U.S. dollar denominated assets.
47