Starbucks 2010 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2010 Starbucks annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations and borrowings as of October 3, 2010, and the timing
and effect that such commitments are expected to have on our liquidity and capital requirements in future periods (in
millions):
Payments Due by Period
Contractual Obligations(1) Total
Less than
1Year
1-3
Years
3-5
Years
More than
5 Years
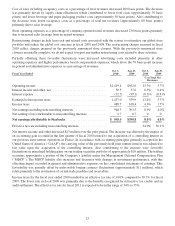
Operating lease obligations(2) ................. $4,084.2 $ 718.4 $1,279.4 $1,006.6 $1,079.8
Debt obligations(3) ......................... 790.8 34.4 68.8 68.8 618.8
Purchase obligations(4) ...................... 613.2 556.7 52.3 4.2 0.0
Other obligations(5) ......................... 107.7 1.8 22.3 9.5 74.1
Total.................................... $5,595.9 $1,311.3 $1,422.8 $1,089.1 $1,772.7
(1) Income tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions were excluded as we are not able to make a reasonably reliable
estimate of the amount and period of related future payments. As of October 3, 2010, we had $68.4 million of
gross unrecognized tax benefits for uncertain tax positions.
(2) Amounts include the direct lease obligations, excluding any taxes, insurance and other related expenses.
(3) Debt amounts include principal maturities and scheduled interest payments on our long-term debt.
(4) Purchase obligations include agreements to purchase goods or services that are enforceable and legally binding
on Starbucks and that specify all significant terms. Purchase obligations relate primarily to green coffee, with
these amounts comprising approximately 90% of the total of this item.
(5) Other obligations include other long-term liabilities primarily consisting of asset retirement obligations, capital
lease obligations and hedging instruments.
Starbucks currently expects to fund these commitments with operating cash flows generated in the normal course of
business.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangement
Off-balance sheet arrangements relate to certain guarantees and are detailed in Note 17 to the consolidated financial
statements in this 10-K.
COMMODITY PRICES, AVAILABILITY AND GENERAL RISK CONDITIONS
Commodity price risk represents Starbucks primary market risk, generated by our purchases of green coffee and
dairy products, among other things. We purchase, roast and sell high-quality whole bean arabica coffee and related
products and risk arises from the price volatility of green coffee. In addition to coffee, we also purchases significant
amounts of dairy products to support the needs of our company-operated retail stores. The price and availability of
these commodities directly impacts our results of operations and can be expected to impact our future results of
operations. For additional details see Product Supply in Item 1, as well as Risk Factors in Item 1A of this 10-K.
FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
Market risk is defined as the risk of losses due to changes in commodity prices, foreign currency exchange rates,
equity security prices, and interest rates. We manage our exposure to various market-based risks according to an
umbrella risk management policy. Under this policy, market-based risks are quantified and evaluated for potential
mitigation strategies, such as entering into hedging transactions. The umbrella risk management policy governs the
hedging instruments the business may use and limits the risk to net earnings. We also monitor and limit the amount
of associated counterparty credit risk. Additionally, this policy restricts, among other things, the amount of market-
based risk we will tolerate before implementing approved hedging strategies and prohibits speculative trading
activity. In general, hedging instruments do not have maturities in excess of five years.
34