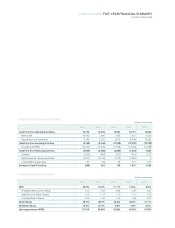
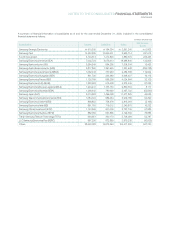
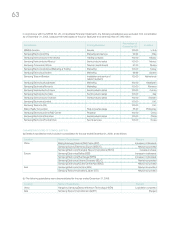
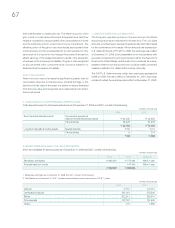
Samsung 2008 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2008 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
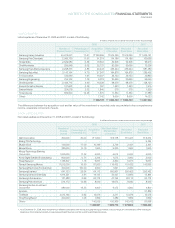
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The significant accounting policies followed by the Company in the
preparation of its consolidated financial statements are summarized
below:
BASIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT PRESENTATION
The Company maintains its accounting records in Korean won and
prepares statutory financial statements in the Korean language in
conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the
Republic of Korea. Certain accounting principles applied by the
Company that conform with financial accounting standards and
accounting principles in the Republic of Korea may not conform with
generally accepted accounting principles in other countries.
Accordingly, these financial statements are intended for use by those
who are informed about Korean accounting principles and practices.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been con-
densed, restructured and translated into English from the Korean lan-
guage consolidated financial statements. Certain information
attached to the Korean language consolidated financial statements,
but not required for a fair presentation of the Company’s financial posi-
tion, results of operations or cash flows or changes in equity, is not
presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
APPLICATION OF THE STATEMENTS OF KOREAN
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
The Company’s consolidated financial statements were prepared in
conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in Korea,
including SKFAS No. 1 through No. 25.
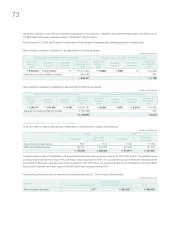
NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
AND ACCOUNTING CHANGES
The Company has changed the scope of its related parties in accor-
dance with revision of SKFAS No. 20, Related Party Disclosures.
Note 29 to consolidated financial statements as of and for the year
ended December 31, 2007 presented herein for comparative pur-
pose, has been restated to reflect this change.
USE OF ESTIMATES
The preparation of the financial statements requires management to
make estimates and assumptions that affect amounts reported
therein. Although these estimates are based on management’s best
knowledge of current events and actions that the Company may
undertake in the future, actual results may differ from those estimates.
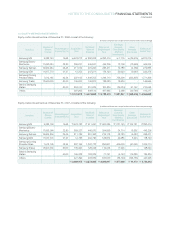
PRINCIPLES OF CONSOLIDATION
The Company records differences between the investment account
and corresponding capital account of subsidiaries as goodwill or
negative goodwill, and such differences are amortized over five
years using the straight-line method. However, differences which
occur from additional investments acquired in consolidated subsid-
iaries are reported in a separate component of equity, and are not
included in the determination of the results of operations. In accor-
dance with the SKFAS No. 25, Consolidated Financial Statements,
minority interests in consolidated subsidiaries are presented within
equity and identified separately from shareholders’ equity in the
consolidated balance sheet.
All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been
eliminated during consolidation. Unrealized profits included in inven-
tories, property, plant and equipment and other assets, as a result of
intercompany transactions, are eliminated. Unrealized profits, aris-
ing from sales by the consolidated subsidiaries, or equity-method
investees, to the controlling companies, or sales between consoli-
dated subsidiaries, or equity-method investees, are fully eliminated,
and charged to shareholders’ equity and minority interests, based
on the percentage of ownership.
The SEC and its consolidated subsidiaries follow the same fiscal
year end. Differences in accounting policies between the SEC and
its consolidated subsidiaries are adjusted during consolidation.
INVESTMENT IN SECURITIES
Investments in equity securities or debt securities are classified into
trading securities, available-for-sale securities and held-to-maturity
securities, depending on the acquisition and holding purpose. Trading
securities are classified as current assets while available-for-sale
securities and held-to-maturity securities are classified as long-term
investments, except those securities that mature or are certain to be
disposed of within one year, which are classified as current assets.
Cost is measured at the market value upon acquisition, including
incidental costs, and is determined using the average cost method.
Available-for-sale securities are stated at fair value, while non-mar-
ketable equity securities are stated at cost. Unrealized holding gains
and losses on available-for-sale securities are reported in equity
under accumulated other comprehensive income, which are to be
included in current operations upon the disposal or impairment of
the securities. In the case of available-for-sale debt securities, the
difference between the acquisition cost after amortization using the
effective interest rate method and the fair value is reported in equity
as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
Impairment resulting from a significant or prolonged decline in fair
value of the security below its acquisition cost, net of amortization is
recognized in current operations.
EQULTY-METHOD INVESTMENTS
Investments in business entities in which the Company has the abil-
ity to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial
policies are accounted for using the equity method of accounting.
Under the equity method, the original investment is recorded at cost
and adjusted by the Company’s share in the net book value of the
investee with a corresponding charge to current operations, a sepa-
rate component of equity, or retained earnings, depending on the
nature of the underlying change in the net book value. All significant
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
CONTINUED