Motorola 2004 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2004 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
60 MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The scope and size of systems requested by some of the segment's customers are increasing, including requests
for country-wide and statewide systems. These larger systems are more complex and include a wide range of
capabilities. Large-system projects will impact how contracts are bid, which companies compete for bids and how
companies partner on projects.
The segment was awarded a number of major, multi-year contracts in 2004, including: (i) a $329 million
contract with the Commonwealth of Virginia for a sophisticated digital voice and wireless data communications
system, (ii) a $294 million contract to provide the U.S. Postal Service with data communications capability, and
(iii) a contract with the Austrian Ministry of Interior to provide a mission-critical, country-wide TETRA public
safety digital radio network.
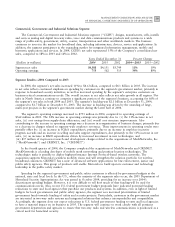
Segment ResultsÌ2003 Compared to 2002
In 2003, the segment's net sales increased 10% to $4.1 billion, compared to $3.7 billion in 2002. The segment's
backlog was $1.7 billion at both December 31, 2003 and December 31, 2002. The increase in net sales was
primarily due to increased spending by customers in the segment's government market, primarily due to homeland
security initiatives. Net sales were also increased by contracts relating to the conÖict in the Middle East and the
reconstruction of public safety systems in Iraq. In 2003, $2.7 billion, or 66% of the segment's net sales, were in
North America, as compared to $2.4 billion, or 65% of the segment's net sales, in 2002.
The segment's operating earnings increased to $562 million in 2003, compared to operating earnings of
$313 million in 2002. The increase in operating earnings was primarily related to: (i) an increase in gross margin,
primarily due to: (a) the 10% increase in net sales, (b) a favorable product mix, reÖecting a higher proportion of
sales of subscriber equipment and a lower proportion of sales of infrastructure equipment, and (c) continued
beneÑts from prior cost-reduction actions, and (ii) a decrease in reorganization of business charges, primarily due
to a decrease in charges related to segment-wide employee severance. These improvements in operating earnings
were partially oÅset by: (i) an increase in SG&A expenditures due to an increase in employee incentive program
accruals, and (ii) an increase in R&D expenditures. Although both SG&A and R&D expenditures increased, SG&A
and R&D expenditures as a percent of net sales decreased in 2003 compared to 2002.
Integrated Electronic Systems Segment
The Integrated Electronic Systems segment (""IESS'') designs, manufactures and sells: (i) automotive and
industrial electronics systems, (ii) telematics systems that enable automated roadside assistance, navigation and
advanced safety features for automobiles, (iii) portable energy storage products and systems, and (iv) embedded
computing systems. In 2004, IESS's net sales represented 9% of the Company's consolidated net sales, compared to
10% in 2003 and 9% in 2002.
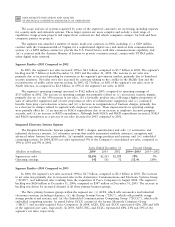
Years Ended December 31 Percent Change
(Dollars in millions)
2004
2003 2002
2004Ì2003
2003Ì2002
Segment net sales $2,696 $2,265 $2,189 19% 3%
Operating earnings 142 161 52 (12)% 210%
Segment ResultsÌ2004 Compared to 2003
In 2004, the segment's net sales increased 19% to $2.7 billion, compared to $2.3 billion in 2003. The increase
in net sales was primarily due to increased sales in the Automotive Communications and Electronic Systems Group
(""ACES''), and additional sales resulting from the acquisition of Force Computers in August 2004. The segment's
backlog was $424 million at December 31, 2004, compared to $347 million at December 31, 2003. The increase in
backlog was driven by increased demand in all three primary business groups.
The three primary business groups within the segment are: (i) ACES, which sells automotive and industrial
electronics systems, including telematics, (ii) the Energy Systems Group (""ESG''), which sells portable energy
storage products and systems, and (iii) the Embedded Communications Computing Group (""ECCG''), which sells
embedded computing systems. As stated below, ECCG consists of the former Motorola Computer Group
(""MCG'') and recently-acquired Force Computers. In 2004, ACES, ESG and ECCG represented 62%, 22% and 16%
of the segment's net sales, respectively. In 2003, ACES, ESG, and ECCG represented 64%, 23% and 13% of the
segment's net sales, respectively.